What is Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)?
People with diabetes often experience symptoms like frequent urination, increased thirst, and fatigue. Whereas people who do not have diabetes or are unaware of the condition may experience these symptoms and not think much of them.
These signs can be easily overlooked or mistaken for something less serious, but they should not be ignored. These symptoms need your attention as they can indicate hyperglycemia, which, if left unmanaged, can lead to more serious health issues.
But what exactly is hyperglycemia, and what should you do to manage it properly? Let’s find out.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia or Hyperglycaemia, or high blood sugar, occurs when the glucose (sugar) levels in your blood are higher than normal. While it’s most commonly linked to diabetes, anyone can experience high blood sugar, especially when the body isn’t using insulin (the hormone that regulates blood sugar) properly.
What is the Blood Sugar Level for Hyperglycemia?
- Fasting (after 8 hours): Higher than 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: Over 180 mg/dL
Hyperglycemia can be episodic, meaning it might not be a constant condition but can occur at certain times, such as after eating a large meal or during illness. This is why it’s important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly, whether you have diabetes or not. Managing these episodes early on can help prevent more serious complications in the future.
Now, you might be wondering why two different kinds of blood sugar levels are mentioned above.
So, depending upon the timing of hyperglycemia, it could be of two types: Fasting hyperglycemia and post-prandial hyperglycemia.
Here’s a general blood sugar levels chart to help you understand what blood sugar levels are considered hyperglycemic:
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
| Test | Normal Blood Sugar Levels |
| Fasting (after 8 hours) | 70 to 99 mg/dL |
| 2 hours after a meal | Less than 140 mg/dL |
Blood Sugar Levels for People with Prediabetes
| Test | Prediabetes Blood Sugar Levels |
| Fasting (after 8 hours) | 100 to 125 mg/dL |
| 2 hours after a meal | 140 to 199 mg/dL |
Blood Sugar Levels for People with Diabetes
| Test | Diabetes Blood Sugar Levels |
| Fasting (after 8 hours) | 126 mg/dL or higher |
| 2 hours after a meal | 200 mg/dL or higher |
Fasting Hyperglycemia vs. Postprandial (After-Meal) Hyperglycemia
Fasting hyperglycemia occurs when blood sugar is high after not eating for at least eight hours. Postprandial hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels that occur after meals, usually 1-2 hours after eating. Both types can be dangerous if not managed properly.
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal TestDiabetes Reversal
Calculator
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia?
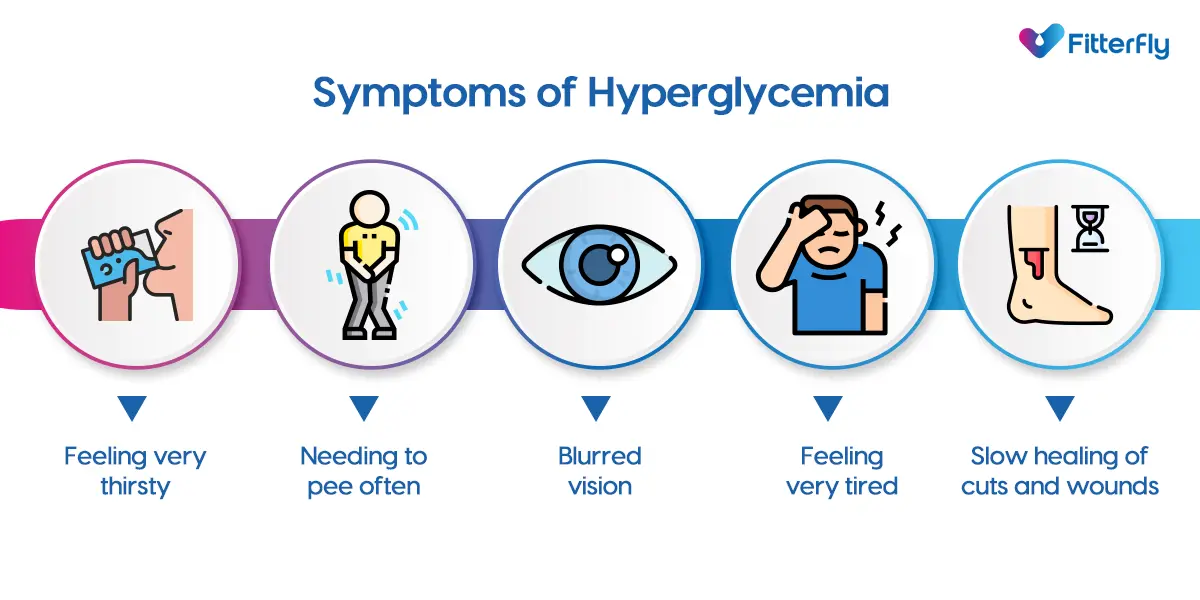
As we mentioned earlier, in most cases, you may not get any symptoms of hyperglycemia, and it may be an incidental finding. However, certain people may experience several common symptoms:
- Feeling very thirsty
- Needing to pee often
- Blurred vision
- Feeling very tired
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
What Causes Hyperglycemia?


There are several common reasons why blood sugar can get too high:
- Missing insulin or diabetes medicine
- Eating too many sugary or starchy foods
- Feeling stressed because of work, family problems, or even after an illness can make your blood sugar higher than usual
- Not exercising enough
- Being sick or having an infection
| Did You Know?
The Dawn Phenomenon and the Somogyi Effect are both related to high blood glucose/sugar levels in the morning, but they happen for different reasons.
Both can cause high morning blood sugar, but the causes are different; one is a natural hormone response (Dawn), while the other is a reaction to low blood sugar during the night (Somogyi). |
What are the Risk Factors of Hyperglycemia?
You might be more at risk for hyperglycemia if you:
- Have diabetes (especially type 1 or type 2)
- Are overweight
- Have a sedentary lifestyle (not getting enough physical activity)
- Experience frequent stress
- Are older, as age can impact how your body processes sugar
What are the Complications of Hyperglycemia?
If hyperglycemia in diabetes is not treated, it can lead to complications like:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (a serious condition where your body starts breaking down fats instead of sugar for energy)
- Damage to nerves, eyes, and kidneys
- Cardiovascular disease (heart problems)
How is Hyperglycemia Diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose hyperglycemia through a blood test to measure your glucose levels. They might also ask for an A1C test, which shows your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
In some cases, your doctor may request a glucose tolerance test or a urine test to gather more information on how your body handles sugar. These tests help provide a clearer picture of your overall blood sugar control and guide treatment plans.
REVERSED Diabetes in 3 months


5.7%
Happy members
EMI
Guarantee
4.8/5
Diabetes Prime Program
How is Hyperglycemia Treated?
Get yourself diagnosed by your doctor and follow the advice given. Don’t try to self-medicate, as it may worsen your health condition.
How Can I Prevent High Blood Glucose/Sugar?
Apart from following your doctor’s advice, making lifestyle changes can help keep your blood sugar in check for the long term. Preventing high blood sugar requires more than just reacting to spikes; it involves developing a strategy for ongoing management.
1. Diet
Focus on a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid high-sugar, processed foods that cause blood sugar spikes. Instead, choose whole grains, vegetables, and low-glycemic index (GI) foods.
2. Exercise
Regular physical activity is key. Try to aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, like walking, most days of the week. Exercise helps your body to use insulin more efficiently, which can help lower blood sugar levels.
3. Stress Management
Stress can directly impact blood sugar levels. Techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation can help you reduce stress and improve blood sugar control.
4. Medications
Stick to your prescribed medication plan. Take insulin or oral medications exactly as directed by your healthcare provider to keep high blood sugar under control.
5. Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to detect any changes early and adjust your management plan as needed.
When to See a Doctor?
Whenever you feel something isn’t right with your body, contact your doctor immediately. Addressing any unusual symptoms early and keeping regular follow-up appointments is essential for sustained health and well-being.
How We At Fitterfly Can Help You?
At Fitterfly, managing hyperglycemia is not just about addressing immediate spikes but about creating a sustainable strategy for long-term blood sugar control. For our enrolled members, we combine expert support with advanced tools to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Our nutrition coaches design meal plans that prioritize low-glycemic foods that are high in fiber and rich in essential nutrients, helping to keep blood sugar levels stable. Our success coaches provide personalized guidance to keep members motivated and committed to their health goals, while our fitness coaches create exercise plans that enhance insulin sensitivity, lowering blood sugar naturally.
Through the Fitterfly Prime Program, members also benefit from Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM), which comes free of cost. This tool provides real-time insights into blood sugar patterns, allowing us to personalize recommendations and ensure better control of blood sugar levels.
By following this structured approach, our members have successfully managed hyperglycemia, improving their overall health and life. If you want to take control of your blood sugar with expert support, give us a missed call at 08068507599 and one of our program advisors will get in touch with you!
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is condition where a person experience high blood sugar, while in hypoglycemia, person experience low blood sugar. Both conditions can cause problems, but while hyperglycemia can be a long-term issue, hypoglycemia usually needs immediate attention because it can cause fainting or seizures.
Does hyperglycemia turn into diabetes?
Not necessarily, but repeated episodes of high blood sugar can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you don’t already have it.
What hormones cause hyperglycemia?
Hormones like cortisol and glucagon (which signals the liver to release stored sugar) can cause hyperglycemia by raising blood sugar levels.
What blood sugar level is hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is generally diagnosed when fasting blood sugar is above 125 mg/dL.
What to eat when sugar is high?
Foods that are high in fiber and low in sugar, like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, can help lower blood sugar naturally.
How do we reduce glucose naturally?
You can lower blood sugar naturally by exercising, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet having whole vegetable and fruits and reducing stress.
What are the symptoms of hyperglycemia?
Symptoms include increased frequent thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurring of vision.
What gland causes hyperglycemia?
The pancreas, which produces insulin, plays a key role in preventing hyperglycemia. When it doesn’t produce enough insulin, blood sugar can rise.




















