What Are the Complications of Diabetes?
People with diabetes are often also prone to several other health issues more common in those with diabetes.
In this article, we will explore the complications associated with diabetes and learn more about the signs and symptoms of any such complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding these will help you spot the signs early, get the proper treatment and care, and prevent some health complications wherever possible.
What Are the Complications of Diabetes?
There are often two types of diabetes complications:
Chronic Complications (Long term)
Chronic complications are the more severe complications that build up over a more extended period of time. If left untreated, chronic complications can worsen and lead to severe damage.
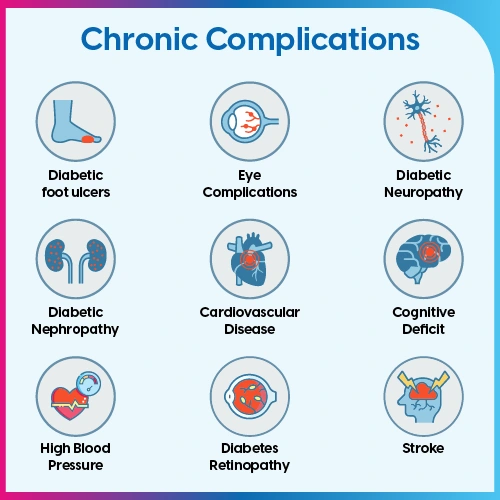
Types of chronic complications with diabetes can be:
1. Nephropathy or kidney damage
- If left untreated, diabetes can cause serious damage to the kidneys over a period of time. This condition is referred to as nephropathy or diabetic nephropathy.
- As a result, the kidneys do not function properly, and it can cause problems in clearing out the excess waste and fluid from your body.
- This is triggered by high blood pressure as well as high levels of blood sugar.
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal TestDiabetes Reversal
Calculator
2. Neuropathy or nerve damage
- High levels of blood sugar over a period of time can also cause significant damage to the nerves. This condition is known as neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy.
- In cases of neuropathy, the brain is unable to send out clear messages to different parts of the body.
- As a result, it can have a direct and, in most cases, serious impact on the ability to move, hear, see, and feel.
3. Retinopathy or eye damage
- In some cases, untreated diabetes over a long period of time can also cause significant damage to the eyes. This is referred to as retinopathy or diabetic retinopathy.
- Retinopathy can cause problems with vision and, in serious cases, can also lead to partial or complete vision loss.
Speak to your healthcare provider and your ophthalmologist about how often you need to get your eyesight tested. Early detection can prevent significant damage to eyesight.
4. Foot problems
- Long-term diabetes, especially without proper treatment and care, can cause serious damage to the feet.
- Nerve or diabetic neuropathy can also aggravate the condition and lead to serious foot damage, sometimes requiring amputation.
- Higher blood sugar levels can damage blood circulation, especially in the feet, and can slow healing.
Routinely inspect your feet for any signs of cuts, sores, or swelling, and immediately inform your healthcare provider if you notice any such signs.
5. Stroke or heart attack
- Diabetes and high blood sugar levels over time can also affect your overall heart health and increase your chances of a heart attack or even stroke.
- This is because high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels, leading to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and stroke.
6. Gum disease or oral diseases
- When there is an excess of sugar in your blood, it can increase the amount of sugar present in your saliva.
- Excess sugar in the saliva can attract more bacteria, which produce acids that can attack the enamel on the teeth and damage the gums.
- Over a period of time, this can damage your gums as well as cause other oral diseases.
- In some cases, it can also lead to damage in the blood vessels of the gums and make your gums more prone to infection.
Get your gums and teeth examined by your dentist every six months and inform them about your diabetes history.
7. Sexual Dysfunction
- In some cases, diabetes over a long period of time can lead to various sexual problems in both men and women.
- High blood sugar can restrict the amount of blood that flows to your sexual organs.
- This can lead to problems in getting aroused or cause erectile dysfunction.
- As a result, sexual intercourse can become painful or difficult.
Speak to your doctor about the same, and if required, speak to a sexologist or gynecologist to ease the pain or discomfort.
Acute Complications
Acute complications are the ones that can occur at any time. Acute complications can crop up at any time, but if left untreated, they can become worse and lead to chronic complications.
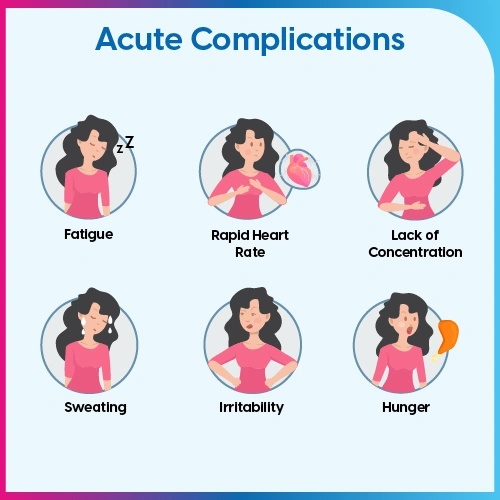

Types of acute complications with diabetes:
1. Diabetic ketoacidosis or DKA
- This happens when there is very high blood sugar and a lack of insulin in the body.
- As a result, it causes a build-up of ketones produced in your liver.
- In some cases, this can lead to an even life-threatening emergency.
2. Blood sugar fluctuations
- Certain blood sugar fluctuations can lead to emergency situations.
- Hypos is when your blood sugar drops too low, and hypers is when your blood sugar levels are too high.
3. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state or HHS
- This is another life-threatening emergency that can occur in people who have type 2 diabetes.
- This can happen when you suffer severe dehydration or have very high blood sugar levels
When Do Diabetes Complications Start?
When diabetes is left untreated, or if you do not take your medicines on time or follow diabetes management tips as suggested by your diabetes healthcare team, it could lead to diabetes complications over a period of time.
Reduced HbA1c by HALF in 6 months


6.6%
Happy members
EMI
Guarantee
4.8/5
Diabetes Prime Program
What Causes Diabetes Complications?
Diabetes can cause different types and intensities of complications in different people, depending on their age, how long they have had diabetes, overall health and lifestyle, type of diabetes, and so on.
- One of the main reasons for diabetes complications is that in people who have diabetes, the amount of glucose in the blood is too high.
- When blood glucose levels are high over a long period, the tissues and various organs in the body start getting affected.
- If left untreated, this can lead to serious damage, and some complications can even be so serious that they can turn life-threatening or fatal.
What are the Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a range of complications that can affect various parts of the body.
- As high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making people with diabetes more susceptible to infections, including those affecting the ears and teeth.
- Skin problems, on the other hand, are a common complication of diabetes, including bacterial and fungal infections, itching, slow wound healing, and a number of other skin conditions.
It’s important for people with diabetes to maintain good hygiene and seek prompt medical attention for any skin, hearing, or dental issues to prevent complications.
How to Prevent Diabetes Complications?
Here are a few things you should keep in mind and adhere to strictly to avoid diabetes complications:
1. Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how you can regularly monitor your blood glucose levels.
- This could be in the form of certain tests that you need to do at the lab or even regular tests that you can easily do yourself in the comfort of your home.
2. Take your diabetes medications on time
- You must take your diabetes medications on time, as suggested by your diabetes healthcare team.
- If you tend to forget to take your medicines on time or are too caught up, set up reminders on your phone for each day and take your medicines accordingly.
3. Understand and follow healthy diet routines
- Speak to your dietician and nutritionist to understand what changes you can bring about in your regular eating habits to help you better manage your diabetes and avoid diabetes complications.
- Depending on whether you are vegetarian or non-vegetarian, your diabetes diet care team can help you create an eating plan that involves healthy, easy, and delicious meals.
You can also check many delicious and healthy recipes on our website and blog.
4. Cut down on smoking and consumption of alcohol
- If you are a smoker, try to quit smoking or start by reducing the number of cigarettes you smoke daily. If you regularly consume alcohol, reduce your daily or weekly drinks.
- Smoking can especially increase the risk of various diabetes complications, such as stroke, eye disease (retinopathy), kidney disease (nephropathy), heart disease or cardiovascular diseases, stroke, nerve damage (neuropathy), foot diseases, and more.
5. Make exercise a regular part of your routine
- Exercise is important when you have diabetes and even otherwise.
- If you have yet to start exercising, start with at least 15 to 30 minutes each day and gradually increase it to an hour. Walking, swimming, aerobics, jogging, and cycling are all great ways to keep exercise a fun part of your daily routine.
FitterTake
Diabetes is not just a singular condition but a complex interplay of factors that can lead to a range of complications, both chronic and acute.
The chronic complications that develop over time can have severe consequences if left untreated, affecting vital organs like kidneys, nerves, eyes, and heart. These complications have the potential to compromise the quality of life and lead to irreversible damage.
This is where Fitterfly comes in to help you take charge and manage your diabetes like a pro. This program, curated by expert diabetologists, nutritionists, physiotherapists, and psychologists, offers a holistic approach to managing diabetes and its associated complications.
Understanding that the journey of diabetes management is unique for each individual, Fitterfly acknowledges the varying factors contributing to complications – age, duration of diabetes, lifestyle, and more.
By tailoring its approach to individual needs, Fitterfly’s Diabetes Care Program offers personalized care that takes into account these factors, ultimately fostering a greater chance of successful management.
For more information, just give us a missed call at 08069450746, and our experts will call you back to help you better.
Your health is your priority, and Fitterfly is here to support you every step of the way.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the complications of untreated diabetes?
Untreated diabetes can lead to a range of complications. Some common ones include kidney damage (nephropathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), foot problems, heart attack, stroke, and even sexual dysfunction. These complications can become severe if diabetes is not properly managed.
What are the acute complications of diabetes mellitus?
Acute complications of diabetes are those that can arise suddenly and require immediate attention. Some examples include diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), dangerous blood sugar fluctuations (hypers and hypos), and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS). These complications can worsen if not treated promptly.
What are the neurological complications of diabetes?
Neurological complications of diabetes, known as neuropathy, involve nerve damage. Depending on the affected nerves, diabetic neuropathy can be: Peripheral neuropathy: This is the most common type of neuropathy. It affects the nerves, particularly in the feet and hands, and can be motor neuropathy, sensory neuropathy, or both. Autonomic neuropathy: This occurs in the nerves that control involuntary functions of the body, such as digestion, urination, or heart rate. Focal neuropathy (Single nerve damage): This affects one nerve at a time, and the symptoms depend on which nerve is affected.
Can you avoid diabetes complications?
Yes, by following a healthy lifestyle, regularly monitoring of your blood sugar levels, taking prescribed medications on time, following a healthy diet plan, quitting smoking or cut down on alcohol, and incorporating regular exercise into your routine, you can avoid or manage the complication of diabetes.
Is diabetes dangerous?
Diabetes can become dangerous when it's not properly managed. If blood sugar levels remain consistently high over time due to lack of treatment or poor management, it can lead to various complications. If they are not treated timely, it can turn out to be a serious impact on your health.





















