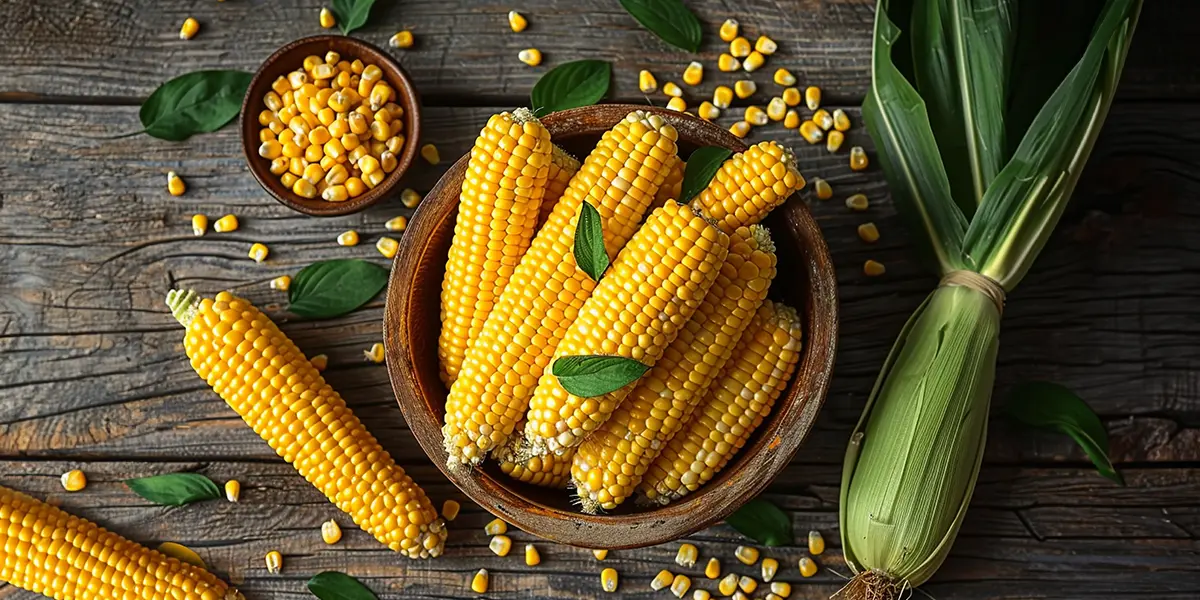
Is Maize (Corn) Good for Diabetes?

When we head to the theater to catch a movie, it’s almost impossible not to crave some snacks to go along with it. The usual suspects are samosas, sandwiches, nachos, vada pav, and of course, popcorn.
If you’re trying to be health-conscious, popcorn often feels like the better choice, it’s not fried, and it’s lighter on the calories, making it an easy pick over the heavier options.
So, if you love having popcorn as a snack or enjoy corn in its various forms, whether it’s roasted desi-bhutta on a rainy day, American bhutta, sweet corn, or even baby corn in your favorite curries, you might be wondering: is it really a good idea to include it in your diet if you have diabetes? Well, you’ve come to the right place.
In this blog, we’ll be answering all your concerns about maize, also known as bhutta, and how it fits into a diabetes-friendly diet. We’ll explore its nutritional benefits, how it affects blood sugar, and the best ways to enjoy it while managing diabetes.
What is Maize (Corn)?
Maize, or corn, is a cereal grain that has been a staple food in many cultures around the world. It comes in various forms, including sweet corn, popcorn, baby corn, and dried corn, which can be ground into flour to make items like makai ki roti or cornmeal porridge. In India, corn is often enjoyed roasted on the cob (bhutta) or boiled as a snack.
Baby corn has many names, like candle corn, cornlettes, young corn, and mini corn. It is the stalk, the immature part of corn or maize. The corb of baby corn is usually eaten whole, whereas the corb of mature corn is difficult to digest by humans.
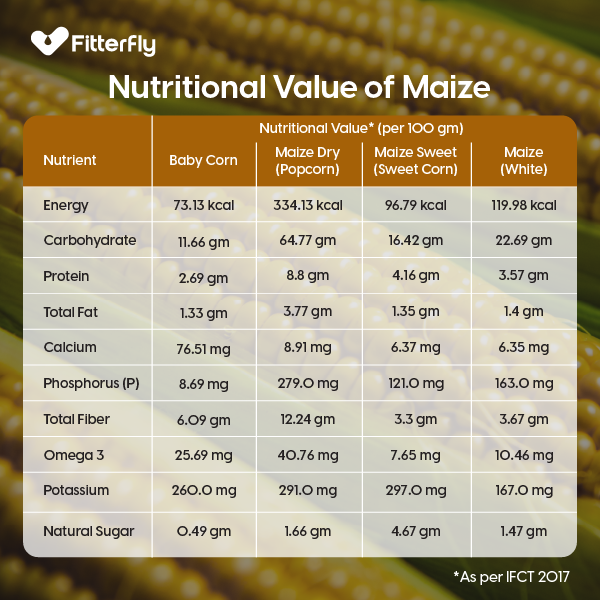
What is the Nutritional Profile of Maize?
Maize is rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins B and C, magnesium, and fiber. According to IFCT (Indian Food Composition Tables), 2017, 100 grams of corn contains:
What is the Glycemic Index of Maize?
The glycemic index (GI) of maize varies depending on how it’s prepared. Boiled whole corn has a low GI of 37, and commonly consumed corn products, such as corn chips and cornflakes, have a high GI in the range of 70–80.
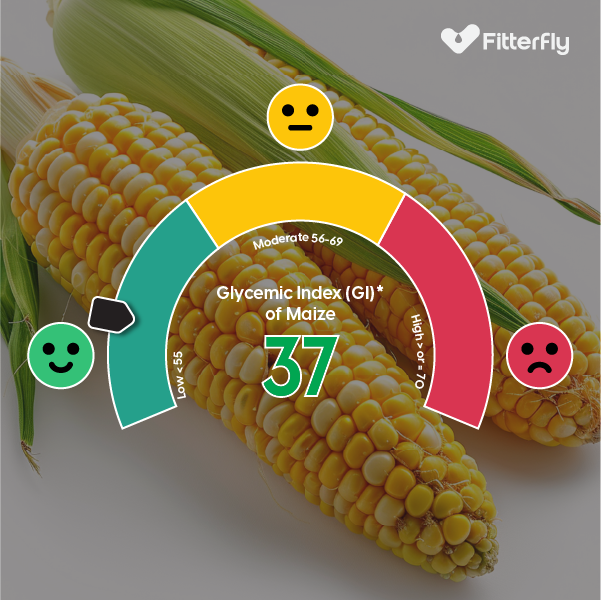

While boiled corn does have a low GI, however in our observations with our members at Fitterfly, we have seen that the personalized glycemic response (PGR) (which is a score given to tell you how individual foods work particularly for you, whether it is good for you or not, does it spike your blood sugar drastically or in acceptable range) to corn and processed corn products tends to be higher in most people, indicating that corn or corn-based food items may cause increases in blood sugar levels for many individuals.
Is Maize Good for Diabetes?
Maize can be a part of a diabetes-friendly diet when consumed mindfully. However, it’s important to note that portion control is key. Overconsumption can still lead to increased blood sugar levels.
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal TestDiabetes Reversal
Calculator
What are the Benefits of Maize for People with Diabetes?
1. Rich in Fiber: The fiber in maize helps slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes in blood sugar levels.
2. Low in Fat: Maize is naturally low in fat, making it a heart-healthy option.
3. Packed with Nutrients: The vitamins and minerals in maize support overall health and can help manage diabetes-related complications.
Which Type of Maize to Choose: Fresh, Frozen, or Canned Corn?
In India, fresh corn is widely available and is the preferred choice for many. Since it’s so easily available as compared to frozen or canned corn, and also retains the most nutrients, it’s best to opt for fresh corn over packaged options like frozen or canned corn.
These packaged varieties are not only less popular but also difficult to find in local markets. They may also contain added ingredients, which is not a great option for your health.
Best Ways to Include Maize in a Diabetes Diet
Maize can be a versatile and enjoyable part of your diet when consumed thoughtfully and in moderation. Here are some diabetes-friendly ways to include maize in your meals:
1. Boiled Corn
While corn is high in carbohydrates, enjoying it in moderation can still be part of a diabetes-friendly diet. Opt for a smaller portion of boiled corn, and enhance the flavor with a squeeze of lemon, a pinch of salt and consume it with a protein-like paneer or boiled chana etc. This can be an occasional snack rather than a regular one.
2. Makai ki Roti
Traditional Indian bread made from maize flour can be enjoyed in moderation. Pair it with fiber-rich leafy greens like sarson ka saag (mustard greens) to balance the meal and minimize the impact on blood sugar levels.
3. Corn Salad
Instead of using a large quantity of corn, mix a small portion of boiled corn kernels with a variety of non-starchy vegetables like cucumber, tomato, and onions. Add some protein like paneer, tofu, egg whites, or boiled channa.
You can squeeze lemon juice and some fresh coriander for a refreshing salad that is lower in carbs and more suitable for a diabetes diet.
4. Corn Soup
When making corn soup, use a minimal amount of corn and focus on adding more low-carb vegetables like spinach or broccoli. Opt for homemade versions where you can control the ingredients, avoiding added thickeners or excessive salt.
5. Bhutte Ka Kees
To make this popular Indore street food more diabetes-friendly, reduce the portion size, modify the recipe to use less milk, and skip any added sweetness. You can still enjoy its rich flavor with a garnish of fresh coriander, grated coconut, and lime.
However, due to its carbohydrate content, it’s best to enjoy Bhutte Ka Kees occasionally.
Practical Tips for Including Maize in a Diabetes Diet
1. Mind the Portion Size
To control your carbohydrate intake, stick to half a cup to one cup of cooked corn per meal.
2. Combine with Protein
Pair maize with protein sources like beans, daals, paneer or tofu, chicken, or tofu to slow the absorption of sugars and maintain balanced blood sugar levels.
3. Choose Whole Corn
Opt for whole forms of corn, like kernels or corn on the cob, instead of processed corn products like cornflakes or corn syrup, which have higher GIs.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
After consuming maize, it’s a good idea to monitor your blood sugar levels to understand how it affects you personally.
How Much Maize (Corn) is Safe for People with Diabetes?
About a quarter cup (approximately 2 to 3 teaspoons) of cooked corn is considered safe for people with diabetes. When eaten as a snack always combine it with a fiber (like green vegetables) and protein (like paneer, daal, eggs, sprouts).
Some people may experience bloating after eating baby corn in excess, and some may be allergic to baby corn.
However, individual responses can vary, so it’s important to monitor your blood sugar and adjust your portions accordingly.
How We At Fitterfly Can Help You?
Corn is a snack we can’t resist, whether it’s a roasted bhutta on a rainy day, popcorn at the movies, or the sweetness of American bhutta. However, managing diabetes while enjoying foods like corn can be challenging. That’s where Fitterfly comes in.
When consumed in moderation and prepared in healthy ways, maize can be part of a balanced, diabetes-friendly diet. Whether it’s makai ki roti, boiled corn, or a fresh salad, it’s important to watch portion sizes and how they fit into your overall carbohydrate intake.
We thoughtfully incorporate corn into our diet plans, pairing it with protein-rich foods like paneer or boiled chana and fiber-rich vegetables like cucumbers or spinach, helping to control blood sugar levels.
Beyond diet, our holistic approach includes personalized fitness and success coaching to keep you on track with your health goals. To learn more about how Fitterfly can help you manage diabetes, give a missed call to 08068507599.
Reduced diabetes medications in 3 months


6.8%
Happy members
EMI
Guarantee
4.8/5
Diabetes Prime Program
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much carbohydrate is in corn?
As mentioned in the table above, the carbohydrate content in corn varies significantly depending on the type and preparation. Dry maize, commonly used for popcorn, has the highest carbohydrate content. cooking method impacts how carbohydrates behave.
Is corn better for blood sugar control than other grains?
Corn has a moderate glycemic index, making it a better option than high-GI grains like white rice.
Is corn high in sugar?
Corn is not particularly high in sugar. The natural sugars in corn are released slowly due to its fiber content, making it a good option for people with diabetes when consumed in moderation.
Can corn be eaten as a snack for diabetes?
Yes, corn can be a healthy snack option. Boiled corn on the cob or a small serving of roasted bhutta with a helping of protein and veggies can be a satisfying and nutritious snack for people with diabetes.
Does maize increase blood sugar?
Maize can increase blood sugar levels, especially if consumed in large quantities or by itself (no accompaniments) in processed forms. However, when eaten in moderation and paired with other low-GI foods, its impact on blood sugar can be minimized.
Does sweet corn increase blood sugar?
Sweet corn has a higher sugar content than regular maize, but it still has a moderate GI. Like other types of corn, sweet corn can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diabetes diet when consumed with protein (like paneer/boiled chana/tofu etc) and fiber (like green vegetables, cucumber, spinach etc).
Is baby corn good for diabetes?
Baby corn is lower in carbohydrates and calories compared to mature corn, making it a good option for people with diabetes when eaten with protein and fiber. It’s often used in salads and stir-fries, providing crunch and nutrition without significantly affecting blood sugar levels. However, as mentioned earlier, some people may experience bloating or allergic reactions after consuming baby corn.





















