Diabetes Polyphagia (Hyperphagia): Sypmtoms, Causes and Treatment

Polyphagia, or excessive hunger, is often linked to several health conditions, with diabetes being one of the most common conditions arising due to high blood sugar levels. If you’re feeling hungry frequently or if you have already been diagnosed with diabetes, it’s essential to get yourself checked to identify the cause and any associated symptoms.
Excessive hunger can also be accompanied by polydipsia (extreme thirst), which may signal the early stages of pre-diabetes or diabetes.
While polyphagia can be triggered by various factors, diabetes is a major cause. So, what exactly is diabetes-related polyphagia? Let’s take a closer look.
What is Diabetes Polyphagia?
Polyphagia, also called hyperphagia, is a condition characterized by extreme and constant hunger. It’s more than just feeling hungry; it’s an overwhelming craving for food, regardless of how much you’ve already eaten. This is commonly seen in people with diabetes, especially when blood sugar levels are poorly managed.
In diabetes, polyphagia happens because the body struggles to use glucose (sugar) for energy. Even if you eat regular meals, your cells aren’t getting the energy they need.
As a result, your brain signals hunger in an attempt to compensate, which can lead to overeating and higher blood sugar levels, creating a difficult cycle to break.
It can also be caused by psychological factors, hormonal imbalances, or other medical conditions.
What are the Symptoms of Polyphagia?
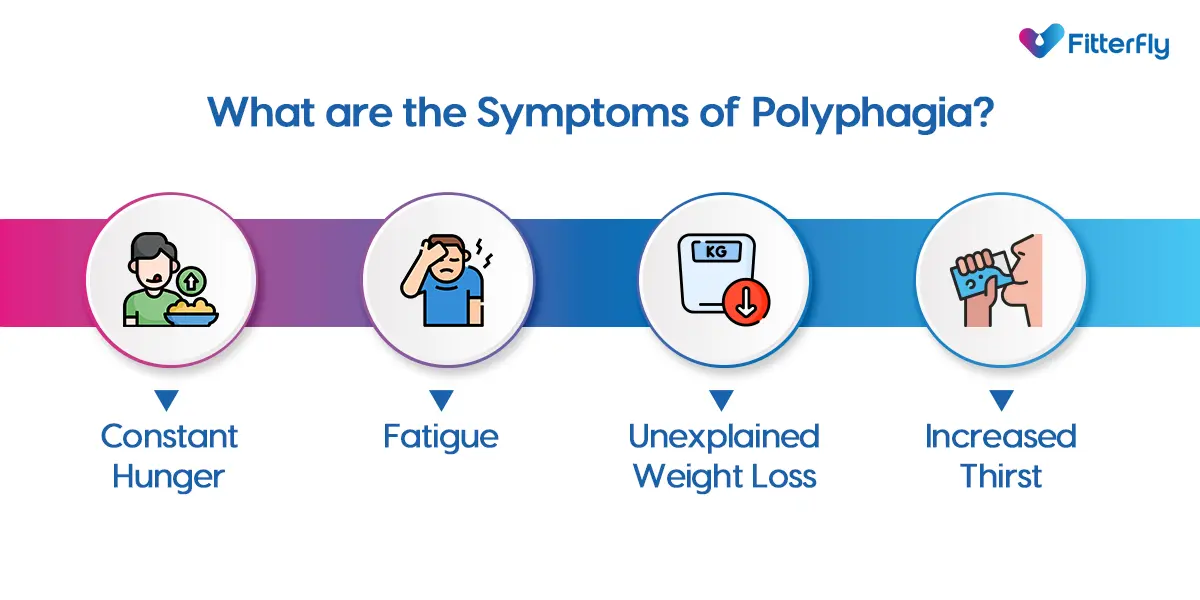
Polyphagia is more than just occasional hunger – it’s persistent and excessive. In diabetes, this can be overlooked or mistaken for stress or a simple love of food.
People often don’t recognize it as a symptom of diabetes, as it doesn’t always come with the typical warning signs. Some common symptoms include:
- Constant Hunger: No matter how much you eat, you feel hungry again shortly after.
- Fatigue: Despite eating more, you feel tired and sluggish because your body isn’t properly using the food for energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Even with increased food intake, you might lose weight as your body burns muscle and fat for energy instead of using the food properly.
- Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst is another sign of high blood sugar, often accompanying hunger.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms regularly, it’s important to check your blood sugar levels and consult your doctor.
What Causes Polyphagia (Hyperphagia)?
Excessive hunger happens because diabetes affects how your body uses sugar for energy. When your blood sugar is high, your body can’t use it properly. This usually happens because:
- Insulin resistance: Your body doesn’t respond well to insulin.
- Lack of insulin: There isn’t enough insulin to move sugar into your cells.
Without energy from sugar, your body’s cells stay “hungry,” even though there’s a lot of sugar in your blood. It’s like having food but not being able to eat it.
This can also happen if you lose calories, have low blood sugar, or lack important nutrients and minerals. Your brain senses this lack of energy and keeps making you feel hungry, even if eating doesn’t solve the problem.
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal TestDiabetes Reversal
Calculator
What is the Diagnosis of Polyphagia?
To diagnose polyphagia, your doctor will review your symptoms and may conduct a blood test to check your blood sugar levels. If your blood sugar is high (over 180 mg/dL), it could indicate uncontrolled diabetes, and polyphagia may be a symptom.
Your doctor will also ask about your eating habits, thirst, fatigue, weight loss, and family history of diabetes. The diagnosis is typically based on your symptoms, medical history, and blood test results.
Fitterfly – What is the HbA1c
How is Polyphagia Treated?
To manage your polyphagia effectively, it’s essential to consult your doctor and strictly follow their guidance. Your doctor may recommend certain lifestyle changes, which could include:
1. Balanced Diet
Eating meals that include fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins helps stabilize your blood sugar and reduce hunger. Avoid sugary or processed foods that cause blood sugar spikes and worsen hunger.
For example, instead of sugary snacks like sweets or biscuits, opt for whole wheat roti with vegetables or a bowl of dal with brown rice. Avoid rice and roti, having both in the same meal.
2. Healthy Snacking
Instead of sugary, fried, or high-fat snacks, opt for low-sugar, nutritious options like fruits, nuts, and whole grains. Healthy snacks like a handful of roasted chickpeas, a fruit like a papaya or an apple, or a small portion of yoghurt with flaxseeds help prevent overeating and support better blood sugar control.
3. Regular Exercise (Fitness Coach)
Physical activity plays a key role in improving insulin sensitivity and helping your body use glucose more effectively. Regular exercise reduces hunger and maintains healthy blood sugar levels. A brisk walk after meals or yoga postures like Surya Namaskar can help keep your blood sugar stable.
4. Adequate Sleep
Sleep deprivation can disrupt hunger-regulating hormones, leading to increased appetite. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night helps manage hunger and keeps your blood sugar stable.
5. Stress Management (Success Coach)
Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels and lead to emotional eating or overeating. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or journaling can help you manage cravings and hunger.
For example, try taking a few minutes to practice mindful breathing or use apps for guided meditation.
6. Consistent Meal Timing
Eating smaller, balanced meals at regular intervals throughout the day helps maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevents sudden hunger spikes.
For example, have a light snack like roasted nuts or a cucumber salad mid-morning, followed by a hearty lunch like chapati with vegetable sabzi and salad or a bowl of mixed vegetable khichdi, salad, dal and curd.
7. Portion Control
Monitoring portion sizes—especially for carbohydrates—helps prevent overeating and ensures blood sugar levels stay stable. For example, instead of large servings of rice, try limiting portions and pairing it with more vegetables and lean proteins like grilled chicken or paneer.
8. Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar checks are essential to understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and other lifestyle factors. Monitoring helps you and your doctor adjust your treatment plan to ensure your blood sugar stays within the target range.
9. Medication Adjustment
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough to control polyphagia, your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medications, such as insulin or other blood sugar-lowering drugs. Proper medication management is crucial in reducing hunger and improving blood sugar control.
10. Carbohydrate Management
It is important to choose complex carbohydrates like whole wheat, brown rice, and quinoa, as well as vegetables like sweet potatoes and carrots. These break down slowly and prevent rapid blood sugar spikes, which can lead to increased hunger.
11. Hydration
Dehydration can worsen feelings of hunger and cause blood sugar fluctuations. Drinking enough water throughout the day supports blood sugar regulation and can help reduce the constant urge to eat.
Consider drinking water, coconut water, or unsweetened herbal teas like mint or ginger tea.
Reduced diabetes medications in 3 months


6.8%
Happy members
EMI
Guarantee
4.8/5
Diabetes Prime Program
When to See a Doctor?
As mentioned earlier in the blog, if you’re experiencing persistent hunger, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or excessive thirst, it’s important to consult a doctor. These could be signs of polyphagia or uncontrolled diabetes.
If lifestyle changes or diet adjustments don’t seem to improve your symptoms, it’s time to seek medical advice. A doctor can help with proper diagnosis, treatment, and blood sugar management, preventing further complications.
How We At Fitterfly Can Help You?
As our expert doctors at Fitterfly always emphasize, prevention is better than cure. So, whenever you feel something might be wrong with your health, it’s always best to consult your doctor and follow their guidance.
At Fitterfly, we are committed to supporting you in managing and preventing health conditions like diabetes through personalized care. Our team of expert Nutrition, Fitness, and Success Coaches work together to help you create a sustainable lifestyle that focuses on balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and stress management.
With our customized plans, you can take control of your health, reduce risks, and manage symptoms effectively. Our goal is not just to help you with treatment but to empower you to make proactive choices that will improve your overall well-being and prevent future health issues.
Call us at 08068507599 to know more about how we can help you better manage your diabetes.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 P's of diabetes?
The 3 P's of diabetes are polyuria (excessive urination), polydipsia (extreme thirst), and polyphagia (excessive hunger). These are common signs of uncontrolled diabetes.
How to stop diabetes hunger?
To manage diabetes hunger, focus on eating balanced meals that include fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Staying hydrated, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, and following your doctor’s prescribed treatment plan can help reduce constant hunger.
Why does polyphagia occur in diabetes mellitus?
Polyphagia occurs in diabetes mellitus because high blood sugar levels prevent glucose from entering the cells, leading the body to signal hunger in an attempt to obtain energy. However, the body can't properly use the food you eat if your blood sugar is not controlled.
Is polyphagia a symptom of diabetes?
Yes, polyphagia is a common symptom of diabetes, especially when blood sugar is not well-regulated. It indicates that the body is not getting the energy it needs, leading to excessive hunger.




















