The Role of Insulin in Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
While most people today know insulin is responsible for controlling blood sugar levels, not much is discussed about the hormone, how it functions and the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels.
Before insulin was discovered, people with diabetes did not live very long. Scientific research resulted in the discovery that a chemical substance produced by the islets of Langerhans cells in the pancreas was missing in people with diabetes.
With the existing research, Banting and Best were able to discover that insulin was a life-saving hormone for people with diabetes. This went on to the development of the first synthetic insulin, and the rest was history!
Basics of Insulin
1. What is insulin?
Insulin is an important hormone produced by the pancreas and helps keep blood sugar levels within the normal range.
2. Where is insulin produced?
Insulin is produced in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans cells in the pancreas organ situated in the abdomen. The amount of insulin produced depends upon your blood sugar levels.
3. What does insulin do?
We get glucose from the food we eat, which causes the blood glucose levels to rise right after we eat. In times of need (like fasting), the liver makes glucose and releases it into the blood. To restore blood glucose levels, the pancreas releases insulin.
The higher your blood sugar levels, the more insulin is produced. However, high or exceptionally low insulin levels for prolonged periods of time are not good for your health. A delicate balance of insulin ensures all body systems function optimally.
Besides blood sugar regulation, another role of insulin is that it regulates fat metabolism in the body.
Insulin works closely with another hormone produced by the pancreas called glucagon. Glucagon is produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas and plays a vital role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
While the pancreas produces insulin to prevent a spike in blood sugar levels, glucagon prevents the blood glucose levels from dropping too low.
A delicate balance of these hormones ensures your blood glucose levels remain within the normal range.
Insulin and Diabetes
Two common issues with insulin can result in diabetes, namely:
1. Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the cells in the liver, muscles and fat do not respond to the hormone and are unable to take up glucose from the blood. This causes high blood sugar levels, causing the pancreas to make more insulin.
As long as the insulin produced by the pancreas is able to maintain produce insulin, blood sugar levels will continue to remain within the normal range. However, when the insulin resistance of cells continues for a long time, it will eventually damage the pancreas and result in type 2 diabetes.
If insulin resistance is not treated early, later it can lead to insulin deficiency.
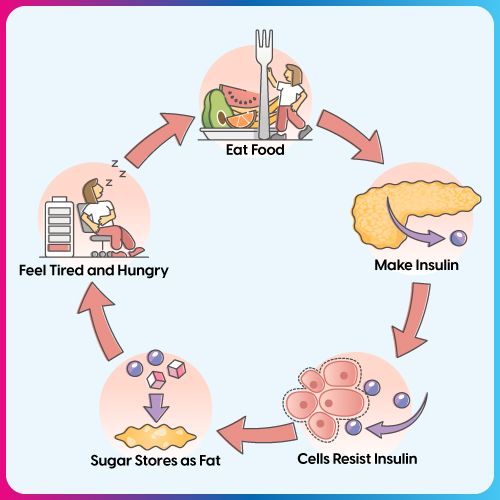

2. Insulin deficiency
Though blood glucose levels are the most important factor that determines insulin secretion, several factors govern the process. Insulin deficiency is a condition in which there is a decrease in the hormone production rate by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Absolute insulin deficiency is seen in type 1 diabetes whereas, partial insulin deficiency is observed in long-standing uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Both these conditions are treated using synthetic insulin in the form of insulin shots (injections).
Insulin-related diseases
Abnormal insulin production has been related to several conditions, and the most common ones are:
1. Diabetes
One of the most common conditions associated with insulin production is diabetes mellitus or type 2 diabetes. This condition can be further divided into three types, namely:
a. Type 1 diabetes
In these individuals, autoimmune conditions set in to destroy the insulin-producing pancreatic cells, resulting in insulin deficiency. These individuals require external supplementation of insulin to maintain their blood sugar levels within the normal range.
b. Type 2 diabetes
In this condition, especially long-standing uncontrolled diabetes, the body is unable to produce adequate amounts of insulin, resulting in insulin deficiency. Factors like genetics, obesity, lifestyle factors and lack of exercise are some reasons that can cause type 2 diabetes.
c. Gestational diabetes
Due to the hormonal changes pregnant women undergo, they may develop insulin resistance during pregnancy. This situation resolves after childbirth.
2. Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of several clinical disorders and may include conditions like prediabetes- the precursor of diabetes mellitus.
3. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Many women with PCOS also exhibit a few features of metabolic syndromes, such as obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidaemia (deranged lipid and cholesterol levels). Having PCOS increases a woman’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Insulinoma
Tumours of the beta cells in the pancreas can result in excess insulin production, which can result in hypoglycemia. However, blood glucose levels alone are not diagnostic of insulinoma.
FitterTake
Insulin is a critical hormone in the body and for diabetes management. While the hormone plays a role in maintaining optimum blood sugar levels, its absence or deficiency can disrupt the normal metabolic process in the body.
Synthetic insulin or insulin injections are effective in helping people with type 1 and some people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels and maintain them within the optimal range.
However, to maintain optimum insulin secretion, it is important to follow lifestyle modification recommended by your diabetes care team at the earliest.
Understanding the role of insulin and how it works in maintaining optimum blood sugar levels is essential for people who wish to manage their diabetes better.
Have queries or concerns regarding diabetes management? Sign up for our program to know more. Need assistance with diabetes? Check out Fitterfly’s Diabetes Care Program, curated by expert diabetologists, nutritionists, fitness specialists, and expert coaches. Just give us a missed call at 08068507599 to speak with us, and we will get back to you.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Don’t struggle alone & get the expert care you deserve






















