The Future of Diabetology: How is AI Reshaping Healthcare Practices
Abstract:
AI in diabetes management is transforming its landscape, offering solutions to challenges like insufficient consultation time and logistic barriers. Automated retinal screening, predictive risk stratification, and AI-designed algorithms, like closed-loop insulin delivery systems and continuous glucose monitoring improve glycaemic legacy among patients and help diabetologists in precision medicine, fueled by AI.
AI is Revolutionising Diabetes Management
The application of AI is revolutionising the diagnosis, treatment, and management of endocrine disorders, including diabetes. With its ability to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions, AI in diabetes management is empowering physicians to deliver personalised care, improve patient outcomes, and advance our understanding of complex hormonal conditions.
Artificial intelligence algorithms in diabetes care help in understanding and predicting individual phenotypes from a big and diverse quantity of clinical and “omics” data. Several branches of science, including genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, lipidomics, and epigenomics, that analyse proteins, RNA, genes, metabolites, lipids, and methylated DNA or modified histone proteins come under “omics” data. They play a crucial role in precision medicine taking into account differences in people’s genes, environments, and lifestyles in the treatment process. Figure 1 denotes the role of machine learning in precision medicine.
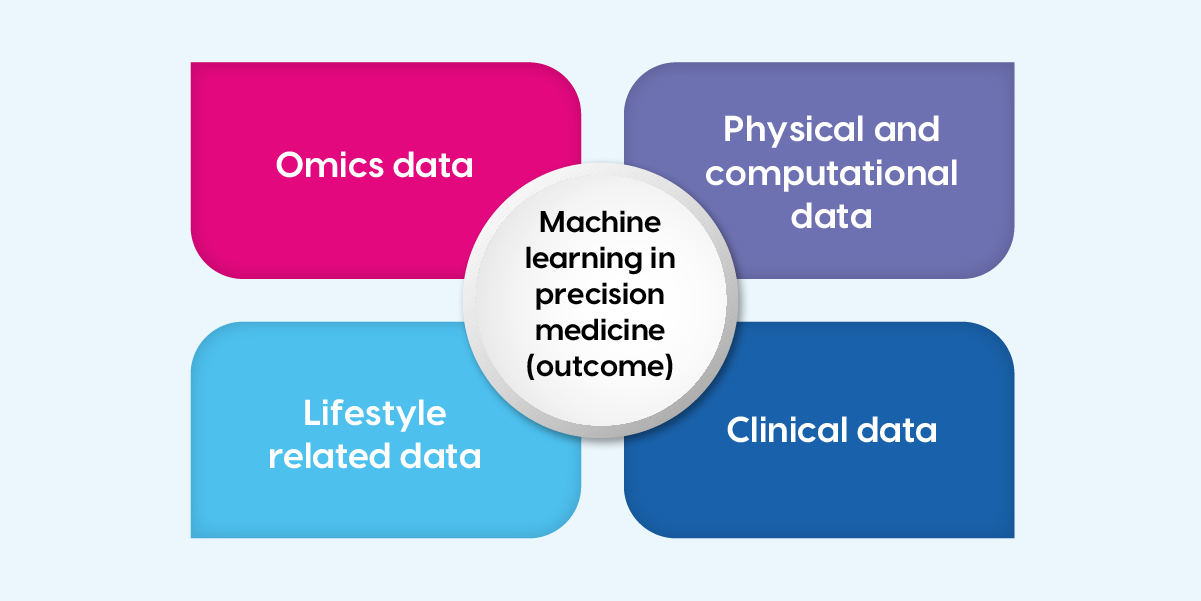
Figure-1 Population data is used in large quantities in precision medicine (PM). Through a wide range of information, including genomics and clinical data, PM seeks to construct a framework for improved healthcare management. The most widely used AI approach in PM is machine learning.
Challenges Associated with Treating Diabetes
In the last two decades, the prevalence of diabetes has exponentially increased globally and is a serious public health issue. By 2030, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimates there will be 552 million diabetics worldwide. Despite the huge burden of this disease, physicians often struggle to address the need gaps in care management, including insufficient consultation time, logistic barriers, an increase in the disease’s complexity and lack of compliance among patients. AI harnesses the potential to solve a majority of these obstacles.
Influences of AI in Diabetes Care
Clinical Diabetology may undergo a revolution driven by improved big data use, more accurate diagnosis of diabetic complications, and lower healthcare costs. Precision medicine’s “digital diabetes” is now possible because of AI and big data.
Automated retinal screening, clinical decision support, predictive population risk stratification, and patient self-management tools are some of the artificial intelligence diabetes care applications.
In genomics and system biology, AI has advanced significantly and continues to advance through the development of new machine learning algorithms. Electronic medical records, also known as health records, are potent instruments for precision medicine, as well as for early detection and prevention, thereby increasing their clinical value and lowering healthcare costs.
Role of AI in the Prediction of Diabetes and Glycemic Events
Prediction of diabetes and glycemic events, diagnosis of complications, and glycemic control are the aspects of diabetes care that are roughly possible through AI.
Examples of AI-designed algorithms include the creation of closed-loop insulin delivery systems and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), which anticipate glucose level status and insulin dosing in response to glucose levels, respectively. Since multiple therapy alternatives must be introduced consecutively, T2DM treatment is more challenging than T1DM treatment. Maintaining strict glucose management and monitoring will slow the development of diabetes and any potential consequences.
Artificial Pancreas Automates Insulin Administration
Due to unexpected exogenous events (such as meal intake), the most challenging aspect of glucose management for type 1 diabetes is the automation of insulin treatment. The artificial pancreas (AP), also known as closed-loop control, is a diabetes management system that measures blood glucose levels using a CGM and automatically administrates the insulin when needed by an insulin pump. It works like a real human pancreas system.
A study suggested that a novel reinforcement learning (RL) based artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm for a fully automated artificial pancreas (AP) system successfully automated blood glucose control with unannounced meal intake.
The pooled analysis of three randomised control trials (RCTs) showed that Control-IQ helped people with type 1 diabetes across a wide range of participant characteristics, including being from a racial or ethnic minority, having lower socioeconomic status, not having used an insulin pump before the study, and having high HbA1c levels.
AI can Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends screening for diabetic retinopathy (DR), the most common microvascular complication in diabetes patients, prior to vision loss.
Because of its high sensitivity in detecting retinopathy, retinal imaging is a widely used screening method. As a result, automated grading of retinal images has been developed to enhance retinopathy screening’s effectiveness. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy requires artificial intelligence based on deep learning and artificial neural network approaches. These methods can detect diabetic retinopathy’s severity as moderate or worse with high sensitivity and specificity. To identify DR symptoms, algorithms for automated grading of retinal images have been developed. The IDx-DR 2.0 retinopathy detection device from IDx LLC in Iowa City, Iowa, USA, is one such AI/ML-based algorithm that has been commercially introduced and received FDA approval.
DreaMed Diabetes- FDA-approved DiabetesSolution
DreaMed Diabetes is another FDA-approved AI-based remote diabetes solution. It provides personalised optimisation for diabetes patients’ insulin therapy management. Information from glucometers, insulin pumps, and event-oriented data is the subject of AI-driven analyses.
A machine learning approach pointed out the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial to identify the factors contributing to variation in all-cause mortality among subjects in this trial. The application of AI algorithms for image-based diagnosis, picture segmentation and reconstruction, image quality control, patient prognostication, phenogrouping, and scientific discovery has been widespread. Demographic and co-morbidity information about the patient enhanced the effectiveness of ML algorithms. In cardiology, AI-based software devices and risk assessment systems have also been used.
Role of AI in Monitoring Diabetes Kidney Disease
A study established an artificial intelligence (AI) system with auto verification and auto guidance subsystems for the detection of urine microalbuminuria (Uma) to monitor the progression of diabetes kidney disease (DKD) and improve laboratory physician efficiency. The urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) and urine microalbuminuria are included in the Uma detection. The auto guidance subsystem offers a series of recommendations to the clinician regarding the diagnosis or further treatment of DKD following verification of the detection results by the auto verification subsystem.
The integration of artificial intelligence in diabetes treatment is transforming the field by providing clinicians with powerful tools to enhance diagnosis, treatment, and patient management. The ability of AI algorithms to analyse large datasets, predict outcomes, and personalise care is revolutionising the way endocrine disorders are understood and managed. While AI holds immense promise, it is essential to ensure ethical implementation, data privacy, and validation of algorithms to maintain patient safety and trust. As AI continues to advance, its potential to improve the lives of individuals with endocrine disorders and drive breakthroughs in the field remains vast.
Key Takeaways
The blog highlights how AI is revolutionizing the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diabetes by leveraging its ability to process vast amounts of data. Here are the key takeaways:
- The integration of AI and big data in precision medicine analyses individual differences in genes, environments, and lifestyles to provide personalised care.
- Automated retinal screening, predictive risk stratification, and the development of closed-loop insulin delivery systems improve patient outcomes by leveraging AI in diabetes care.
- AI plays a crucial role in preventing complications like diabetic retinopathy by early screening.
- Though AI in diabetology has a transformative impact, ethical implementation and considerations for patient safety is crucial in the journey ahead.
About Us
Fitterfly is on a mission to fuel the global metabolic health revolution through the power of Digital Therapeutics (DTx). We partner with physicians to deliver advanced customised digital therapeutics solutions aimed at enhancing the health outcomes of their patients.
By partnering with Fitterfly, you can save time in your clinics, ensure continuity of care for your patients, get research publications, and also enhance your revenue. To know more, please fill out the form below or call us at 080-47093933.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Want to know how can Fitterfly enhance your practice and improve patient outcomes?




















