Is Coffee Good for Diabetes?

My friend, who is from South India, and I met after a long time. We went to a restaurant and ordered coffee.
When we received our cups, he was a little surprised that this coffee was different from what he was used to in South India. He explained that in the South, people often use freshly ground coffee beans to make their coffee. I told him that we typically use pre-packaged, powdered coffee in the northern region.
This difference in coffee preparation reflects the broader variety of coffee options available across India, from instant coffee to freshly ground coffee beans.
People with diabetes need to understand how different coffee preparations can affect their blood sugar levels, whether it’s powdered coffee, instant coffee, or coffee made from freshly ground beans.
In this blog, we will answer the question: Is coffee good for people with diabetes? Let’s start by understanding what coffee is.
What is Coffee?
Coffee is a brewed beverage made from roasted coffee beans, which are the seeds of berries from the coffee plant. There are various types of coffee, including:
1. Instant Coffee: Made from brewed coffee that has been freeze-dried or spray-dried into granules.
2. Ground Coffee: Made by grinding roasted coffee beans, typically used in drip coffee makers (South Indian Filters), French presses, and espresso machines
3. Whole Bean Coffee: Coffee beans that are roasted but not ground, allowing for a fresher taste when ground just before brewing
4. Decaffeinated Coffee: Coffee with most of the caffeine removed, suitable for those sensitive to caffeine.
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal TestDiabetes Reversal
Calculator
What is the Nutritional Value of Coffee?
The nutritional value of coffee varies based on its preparation method, as coffee itself is an ingredient rather than a final product. When consumed without additives like sugar or milk, coffee is low in calories and contains no carbohydrates, fats, or protein.
The nutritional content changes significantly when different types of coffee drinks are prepared. Below is a table comparing the nutritional values of various coffee beverages:
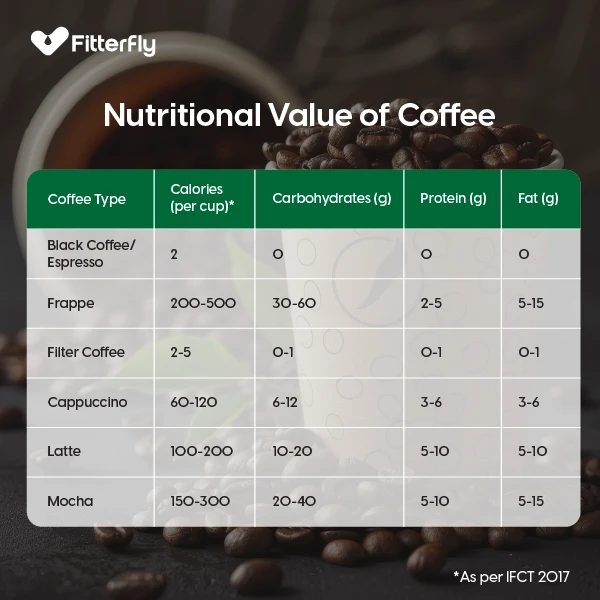
Note
- The nutritional value may vary depending on how the coffee is made and how accompaniments (like milk, sugar, sweeteners, cream etc) are added.
- *1 Cup = 200-250 ml (approx) (International value)
What is the Glycemic Index of Coffee?
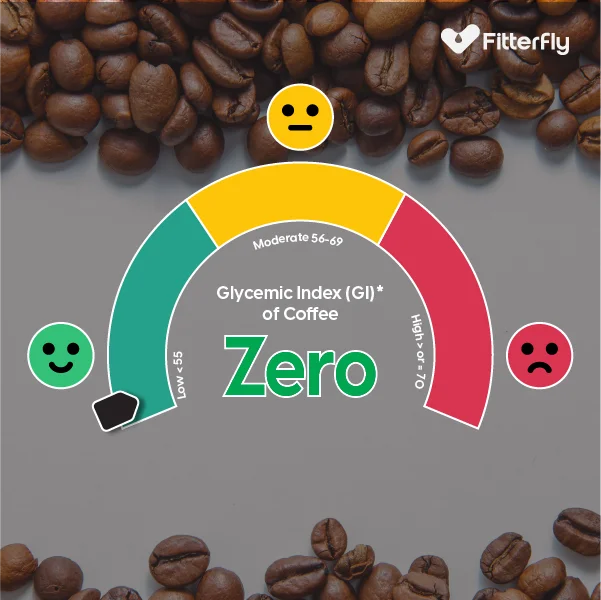

The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Black coffee has a GI of zero because it contains no carbohydrates, which means it does not cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
However, the GI will vary when different types of coffee are made. ingredients like milk, sugar, or cream impacts the overall GI of the coffee, depending on the quantity added.
Is Coffee Good for Diabetes?
For people with diabetes, it’s essential to consider how coffee affects blood sugar levels. Black coffee, without added sugar or high-fat milk, can be a good choice for people with diabetes.
However, coffee’s impact on blood sugar can vary from person to person, so it’s important to monitor how your body responds.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
1. Caffeine Content
Caffeine can impact blood sugar levels differently for everyone.
- Studies show conflicting data regarding the impact of coffee consumption on diabetes.
- Some studies suggest that caffeine might impair insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels, while other studies show it can have beneficial effects.
Therefore, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels when you consume coffee to see its impact on your body.
2. Additives, Sugar, and Sweeteners
Most people add sugar, flavored syrups, or high-fat dairy products to their coffee, which can significantly increase the calorie and carbohydrate content.
For people with diabetes, it’s important to limit these additives or use lower-calorie alternatives such as non-nutritive sweeteners (like stevia), low-fat milk (like toned milk), or plant-based milk (like almond milk).
3. Antioxidants
Coffee is rich in antioxidants (like chlorogenic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, melanoidins etc) which can help reduce inflammation and protect against various diseases, including heart disease and certain cancers. These antioxidants might also help improve insulin sensitivity.
Are There Any Benefits of Drinking Coffee in Diabetes?
There are some potential benefits of drinking coffee for people with diabetes:
- Antioxidants: Coffee is rich in antioxidants, which can help fight inflammation and protect your cells.
- Metabolism Boost: Coffee can increase your metabolism, which can help with weight management.
What are the Other Health Benefits of Drinking Coffee?
Research says that drinking a cup of coffee before studying can help you remember information for over 24 hours.
Beyond diabetes management, coffee offers several other health benefits. Some of them are:
- Enhanced Physical Performance: The caffeine in coffee can increase adrenaline levels, helping you perform better in physical activities.
- Mental Alertness: Coffee can improve focus and concentration, making it a popular choice for boosting productivity.
- Liver Health: Regular coffee consumption has been linked to a lower risk of liver diseases, including liver cancer.
According to studies, drinking two cups of coffee a day can lower the risk of liver cancer by 43%.
Are There Any Risks of Drinking Coffee in Diabetes?
While coffee has several health benefits, there are also some risks to consider:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Some people may experience jitteriness, anxiety, or sleep disturbances due to caffeine.
- Additives: Adding sugar, high-fat milk, or flavored syrups (like chocolate syrup or caramel syrup) can negate the benefits of coffee and cause blood sugar spikes.
- Digestive Issues: Excessive coffee consumption can lead to digestive problems like acid reflux.
What are the Practical Tips for Including Coffee in a Diabetes Diet?
If you enjoy coffee and want to include it in your diet, here are some tips:
- Choose Black Coffee: Opt for black coffee without added sugar or cream to keep it diabetes-friendly.
- Use Low-Fat Milk: If you prefer milk in your coffee, choose low-fat or almond milk.
- Limit Sweeteners:Use artificial sweeteners or a small amount of natural sweetener if needed.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels: Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see how coffee affects you personally. You can use a glucometer to do this.
REVERSED Diabetes in 3 months


5.7%
Happy members
EMI
Guarantee
4.8/5
Diabetes Prime Program
Few Coffee Recipes for People with Diabetes
Here are a few diabetes-friendly coffee recipes:
1. Iced Black Coffee: Brew a strong cup of black coffee, let it cool, and pour over ice. Add a little amount of almond milk, if required, for additional flavour.
2. Cinnamon Coffee: Brew your regular coffee and add a pinch of cinnamon. This adds flavor without extra calories or sugar.
3. Cold-brew Coffee: Soak coffee grounds in cold water overnight, strain, and enjoy cold-brewed coffee the next day. Serve with a splash of low-fat milk.
4. Ghee Coffee: Brew your coffee as usual and add a teaspoon of ghee (clarified butter). Ghee can add a rich, buttery flavor and is considered to have health benefits, including supporting digestion and providing healthy fats.
Ghee coffee has recently become very famous, with many celebrities consuming and promoting it.
What is the Best Time to Drink Coffee for Diabetes?
Research say, one must avoid having it as the first thing in the morning on an empty stomach. Also, clubbing it with your breakfast is also not a good idea because it can tend to spike blood sugar, mess with digestion, and nutrient absorption from what you’ve had in breakfast.
So, its recommended to have it after half an hour post your breakfast.
Also, we suggest you avoid drinking coffee at night, as it can make it harder for you to sleep. Getting good sleep is very important for managing diabetes, so try to avoid coffee in the evening.
How Much Coffee Can a Person with Diabetes Drink Per Day?
According to the FDA, healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 milligrams of caffeine a day, which is about four or five cups of coffee. However, people vary widely in their sensitivity to caffeine and how quickly they metabolize it.
It’s generally safe for people with diabetes to consume 1-2 cups of coffee per day. Monitor your blood sugar levels and how your body responds to find the right amount for you. Moderation is key.
How We At Fitterfly Can Help You?
Whenever we think of a date or a chat with family or friends, coffee completes all these moments ☕. We love a warm cup in winter, and in summer, we enjoy cold coffee.
Coffee complements every occasion perfectly. However, if you have diabetes, you need to be mindful of what and how much you add to your cup.
Ingredients like full-fat milk, sugar, and cream can increase the glycemic index and affect your blood sugar levels.
At Fitterfly, our nutrition coaches map out your meals and create personalized diet plans that let you enjoy what you love, including coffee. They help our members make smart choices so they can enjoy their coffee without compromising their health
Our coaches guide you on how to balance your favorite drinks with a diabetes-friendly diet.
In addition to nutrition support, our fitness and wellness coaches provide guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. They offer tips on exercise routines and stress management, ensuring comprehensive support for your well-being.
To know more about how we can help you, check our Fitterfly Diabetes Prime Program and take the first step towards better health. You can speak to our program advisors by just giving a missed call on 08068507599.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.




















