Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Difference, Causes and Symptoms
India is the diabetes capital of the world. This number refers to people with Type 2 diabetes. Did you know that is more than one type of diabetes? In this article, we will understand what is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes is the type of diabetes in which your body does not produce insulin because your immune system is attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas.
- It is an autoimmune condition. It is diagnosed with a random blood-sugar test or a glycated A1C test.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
- In type 2 diabetes, the body does not respond to insulin like it should, also known as insulin resistance. This means the glucose cannot enter the cells of your body. Leading to an increase in blood sugar levels.
- Prolonged exposure to increased blood sugar levels can even lead to reduced insulin production. And also lead to serious health complications. It is diagnosed with a random blood-sugar test or an HbA1C test.
Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
The main difference is that type 1 diabetes is a genetic condition and is also known as juvenile diabetes, as it affects children (4-7 years) and teenagers (10-14 years). Whereas type 2 diabetes is a lifestyle metabolic disorder that develops over time.
What Causes Diabetes?
| Aspect | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Cause | Autoimmune reaction leading to destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. | Body becomes resistant to insulin or the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin. |
| Age of Onset | Usually diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age. | Most commonly occurs in adults but is increasingly seen in children and teens. |
| Body Weight | Often normal or underweight at the time of diagnosis. | Often overweight or obese; however, it can also occur in individuals with normal weight. |
| Insulin Production | Little to no insulin production. | Insulin production is usually present but inadequate due to insulin resistance. |
| Symptoms | Rapid onset of symptoms such as frequent urination, extreme thirst, and weight loss. | Symptoms may be mild or absent initially; common symptoms include fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing. |
| Treatment | Insulin injections are necessary for survival, along with dietary management and exercise. | Managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin. |
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
It is a type of autoimmune disease. Most of the time, it is genetic or certain environmental elements.
- In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- As a result, the body is no longer able to produce insulin.
- Type 1 diabetes is often hereditary and is first seen in childhood and adolescence. It can also occur in adulthood over the age of 40.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, your body usually becomes resistant to the insulin that is being produced or there is added insulin deficiency.
- The pancreas produces insulin, but the body is not able to use it effectively.
- The risk factors for type 2 diabetes are age, family history, lifestyle, and obesity.
- The good thing about type 2 diabetes is that with timely diagnosis, the right treatment, and positive lifestyle changes, it can be put into remission.
Early Signs of Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes usually have the same kind of symptoms. Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
- Dry and itchy skin
- Sores, cuts or wounds take longer to heal
- Feeling excessively thirsty, more than earlier
- Frequent need to urinate
- Blurry vision or changes in vision
- Unexplained weight loss
- Excessive fatigue and tiredness
- Hunger levels vary
- Tingling sensation in limbs, especially feet
- In some children, it can also lead to bedwetting
Treatment of Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires careful management. Treatment typically includes lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and insulin therapy. Here’s how people with Type 1 diabetes can manage their condition:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Eat better: Include more dal, chickpeas, and paneer for protein. Add lots of fiber with vegetables like okra (bhindi) and leafy greens (spinach or methi). Choose whole grains like brown rice or millet over white rice and rotis made from whole wheat.
- Get moving: Take daily walks, practice yoga, or join a dance class. Even regular household chores can keep you active.
- Manage stress and sleep well: Meditation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress. Try to stick to a regular sleep schedule.
- Lose weight if needed: A bit of weight loss can make it easier for your body to use insulin. Simple changes like eating less fried food and sweets can help.
- Check your sugar levels often: Use a glucometer to keep track of your blood sugar. This way, you know what foods and activities work best for you.
2. Monitoring
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial. This can be done using traditional blood glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring systems. The frequency of monitoring will depend on the personalised treatment plan and level of blood sugar control.
- Hemoglobin A1C Tests: This test provides an average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months. It helps to understand how well the diabetes is being managed over time. The goal for most people with Type 1 diabetes is to have an A1C level of less than 7%.
Treatment options for Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin therapy
- Insulin Therapy: All people with Type 1 diabetes require insulin to control their blood sugar levels. There are various types of insulin available (rapid-acting, long-acting, premixed), and the type and dosage depend on the individual’s needs.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Some of the most common treatment for type 2 diabetes or management options include
- Lifestyle modification along with proper diet
- Oral medications as suggested by your healthcare provider
- Insulin therapy when required
Risk Factors for Type 1 Diabetes
- Parent or sibling has type 1 diabetes.
- More common in children and adolescents.
- Certain types of genes can affect the chances of type 1 diabetes.
- Geographical areas that are farther from the equator have a higher prevalence of people with type 1 diabetes.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
- Slightly higher levels of blood sugar levels or prediabetes.
- Excessive fat around the belly area.
- Parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes.
- Have PCOS
- Over the age of 45.
- Lead a sedentary lifestyle with no or less exercise.
- Are overweight or obese?
- History of gestational diabetes.
How Does Diabetes Affect the Body and What are the Complications of Untreated Diabetes?
Diabetes affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, this can damage blood vessels and organs, leading to various health complications.
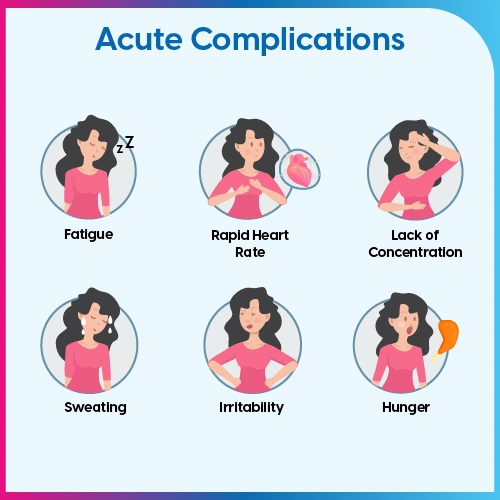
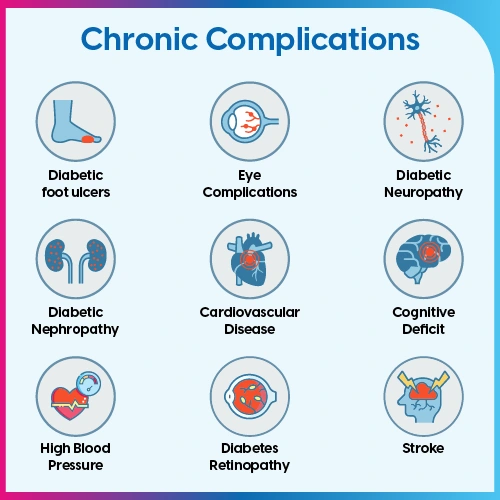
In both cases, untreated diabetes leads your body exposed to high blood sugar, which can result in serious complications.
Some of the common complications are as follows:
| Short-Term Complications | Long-Term Complications |
| Hypoglycemia (Low blood sugar) | Cardiovascular Disease |
| Hyperglycemia (High blood sugar) | Kidney Damage (Nephropathy) |
| Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Eye Damage (Retinopathy) |
| Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State | Nerve Damage (Neuropathy) |
| Foot and Skin Complications |


Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
Diabetes is often seen more as a result of lifestyle choices than a disease. It’s important not to let it cause too much fear or worry. Stress can make diabetes worse, so managing your lifestyle well is key.
Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly. However, Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented as it’s largely due to genetic and unknown factors, but you can manage it well with lifestyle modifications, proper diet and medications.
This is where Fitterfly comes in. We help you manage your diabetes and lifestyle better by using advanced tools like Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and getting advice from experts.
We use CGM technology to constantly check your blood sugar levels. This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and stress affect your blood sugar.
Based on this information, our expert-led team, including nutritionists, endocrinologists, and fitness coaches, creates a plan just for you. This plan doesn’t only help control your diabetes but also aims to improve your overall health.
With the combination of technology and expert advice, Fitterfly helps you make choices that are right for your health. The goal is to change your health with a plan that is tailored to you, leading to a healthier and more balanced life.
Fittertake
Type 2 diabetes can be managed effectively with timely diagnosis and early action. However, to improve your quality of life and avoid future complications.
You should regularly follow up with your healthcare provider to prevent complications and manage the condition effectively. These general check-ups include:
- Routine Blood Sugar Monitoring: To keep track of blood glucose levels.
- HbA1c Testing: Conducted every 3-6 months to assess average blood sugar control.
- Cardiovascular Health Checks: Regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Kidney Function Assessment: Annual tests to evaluate kidney health.
- Comprehensive Eye Exams: Yearly examinations to detect any early signs of eye complications.
- Neurological Exams: Regular checks for signs of nerve damage, especially in the feet.
- Dental Check-Ups: To monitor for gum diseases and other oral health issues.
It is important to have a plan that takes into account all the factors that affect type 2 diabetes.
That includes diet, exercise, sleep, stress, and mental health management. Fitterfly’s Diabetes Prime Program comes with a dedicated coach of nutritionists, physiotherapists, and psychologists to help you manage and reverse your diabetes.
Talk to our Program Advisor to know more or just give us a missed call at 08068507599, and we will definitely get back to you.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Common Is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is less common than Type 2, accounting for about 5-10% of all diabetes cases. It's usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults but can occur at any age.
How Common Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent, making up about 90-95% of all diabetes cases. It's more common in adults, but an increasing number of children, teens, and young adults are being diagnosed due to rising obesity rates.
Diet for Type 1 Diabetes?
A diet for Type 1 diabetes includes balancing insulin with food intake and energy expenditure. It typically involves counting carbohydrates, eating fiber-rich foods, and having consistent meal timing.
Diet for Type 2 Diabetes?
A diet for Type 2 diabetes focuses on controlling blood sugar levels along with weight management through a balanced diet that includes limiting refined carbs and sugars, eating more whole foods, and increasing fiber intake. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and portion control is also crucial.
How does insulin usage differ in type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
In type 1 diabetes, the body produces little to no insulin, so insulin therapy is essential not only for blood sugar control but for survival too. However, type 2 diabetes can be managed with lifestyle modifications and several oral medications or insulin, depending upon your condition.
How do the symptoms of hypoglycemia differ between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
The symptoms of hypoglycemia are generally depends upon the severity of hypoglycemia (shaking, confusion, irritability, hunger, etc.), but the severity and frequency of hypoglycemia might vary between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Is there a hereditary component to both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Yes, the risk of type 2 diabetes is higher when there is a positive with a family history, while type 1 also has genetic links but is less predictable.
Can gestational diabetes lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes later in life?
Yes, gestational diabetes can lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes later in life.
Can pregnancy impact the management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes differently?
Yes, due to various hormonal changes during pregnancy it can impact the management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Is insulin resistance present in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Insulin resistance is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes but if you gain weight, you insulin resistance can be developed in case of type 1 diabetes.
Can stress impact blood sugar levels differently in type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Stress affects both types of diabetes and can lead to fluctuating blood sugar levels.
Can viral infections trigger the onset of both types of diabetes?
Certain viruses are thought to possibly trigger type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible individuals. Type 2 diabetes is more related to lifestyle factors, but infections can exacerbate an already underlying condition.
Can hormonal changes affect blood sugar in type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Hormonal changes can affect both types by altering blood sugar levels. However, people with type 1 diabetes might experience more significant fluctuations due to their body's inability to produce insulin.




















