The Digital Age and Patient Expectations in Diabetes Care: A Physician’s Guide
Abstract
The fusion of digital technology and diabetes management has significantly impacted patient expectations and transformed the physician’s role. It mitigated long-standing challenges in diabetes care, such as the escalating patient-to-doctor ratios and geographical barriers to accessing essential healthcare.
The integration of cloud-connected glucose monitoring systems, artificial intelligence applications, and telehealth services has emerged as a pivotal force in revolutionizing diabetes care. However, the successful implementation of these technologies relies on regulatory frameworks by EMA, USFDA and ICMR.
Digital Technology Making Rapid Strides in Diabetes Care
Digital technology is making rapid advances in all spheres of healthcare, including diabetes management. The HealthTech market in India reportedly expanded at a CAGR of 39% post-pandemic to $ 5 Bn by 2023. Scientists regularly launch innovative health-related smartphone apps to state-of-the-art AI-driven robotic devices to improve patients’ lives.
As physicians navigate the complexities of the digital age, understanding and meeting patient expectations become crucial components of effective care delivery. This blog serves as a guide for physicians, exploring the impact of the digital age on diabetes care and offering insights into addressing patient expectations.
Challenges in Diabetes Care Before Technology Took Over
Before the advent of technology in diabetes care, the healthcare ecosystem was plagued by multiple challenges. Additionally, the global burden of diabetes is increasing exponentially, thus posing more barriers to delivering care.
Worsening Patient-to-Doctor Ratios
According to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s latest report, India has 1 doctor per 834 patients. Though the number of healthcare professionals has improved in the last few decades and is higher than the WHO-recommended 1 doctor to 1000 patients, it is not enough to manage the country’s disease burden.
It often leads to overload among clinicians and miscommunications between patients and doctors. Moreover, many doctors practise traditional forms of medicine like Ayurveda, Homoeopathy, and Naturopathy. WHO and the Indian Medical Association suggested ratio does not include traditional medicine practitioners in their calculations.
Geographical Barriers to Accessing Care
Due to topographical constraints and inadequate infrastructure, rural areas of India often remain deprived of specialised medical care. There are reports of patients travelling long distances seeking expert medical guidance. Moreover, high rates of poverty and non-existent insurance coverage prevent many diabetes patients from accessing the latest treatment options.
Patient Burden
India being the most populous country in the world, demonstrates extreme patient burden of both communicable and non-communicable diseases. It is also the Diabetic Capital of the world, with more than 101 million of its population living with diabetes while an additional 136 million live with prediabetes, as per an ICMR study.
With a population of 140 crores, India’s doctor-to-patient ratio is 1.2. China, with a comparable population load, reported a doctor-to-patient ratio of 2.4. Developed countries like Sweden, Germany, Switzerland, the USA and France demonstrate a much better doctor-to-patient ratio of 7.1, 4.5, 4.4, 3.6, and 3.3 respectively. India requires more qualified doctors and access to digital diabetes management to take care of the huge patient burden.
Economic Burden of Diabetes
The cost of diabetes treatment is continually on an upsurge. A 2023 study indicated that the annual mean total cost of diabetes management stands around ₹49,037. Among these, the highest cost component was the medicine expenditure, around 64% of the total cost. ADA also stated that diabetes patients incur ∼2.3 times higher medical expenditure than patients without diabetes.
Role of Digital Care in Addressing These Challenges
The integration of digital tools in diabetes management has taken care of most of the challenges listed above. The below-mentioned digital diabetes care practices can improve patients’ expectations and outcomes.
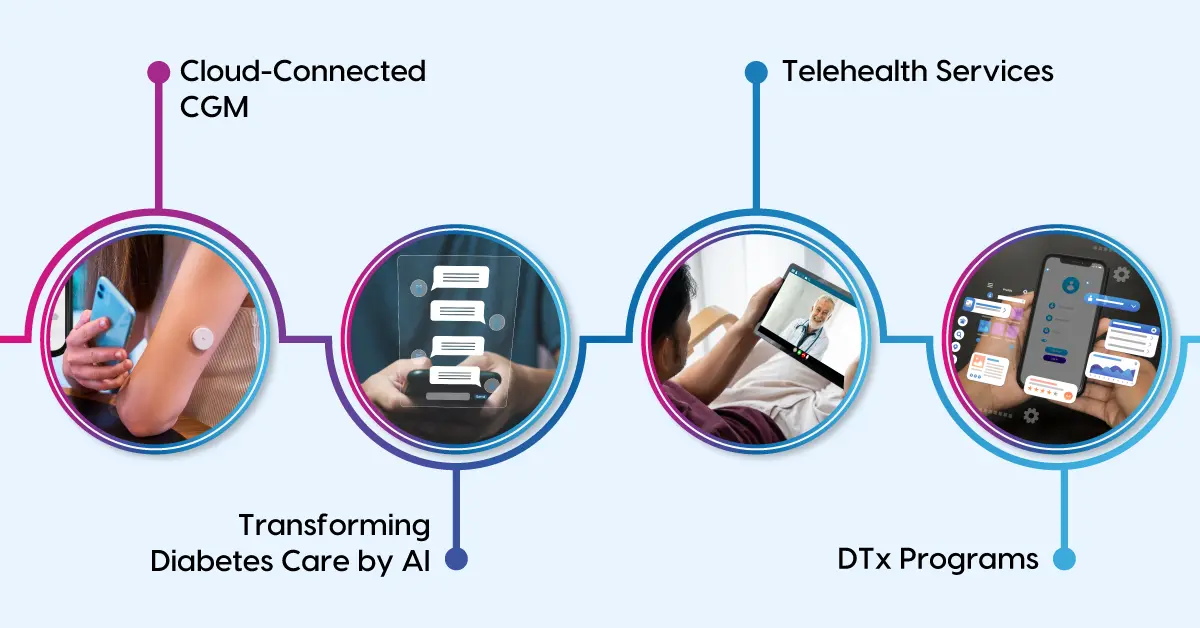
Cloud-Connected Glucose Monitoring Systems
Cloud-connected continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) gadgets transmit patients’ blood sugar data to smartphone apps or Web-based platforms (“the Cloud”) automatically. It has revolutionized glucose monitoring as individuals can keep track of their blood sugar readings digitally via smartphones, smartwatches or tablets painlessly.
These devices utilize a microfilament inserted underneath patients’ skin into the interstitial fluid instead of monitoring blood sugar by painful finger pricks. The filament samples the interstitial fluid every 15 minutes to generate 1344 readings in 2 weeks.
Physicians can also remotely monitor patients’ glucose readings in real-time through these connected devices. They can guide patients during hypo and hyperglycemia without physically travelling to clinics.
The feature is immensely beneficial in rural locations with low doctor-to-patient ratios. Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2 and 3, Dexcom G-7, and Medtronic MiniMed Connect are popular cloud-connected CGM devices.
Fig 1: Different modes of Digital Care to improve patients’ expectations and outcomes.
Transforming Diabetes Care by AI
AI integration has vastly improved diabetes management by minimising challenges like insufficient consultation time and logistic barriers. AI can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions, thus guiding physicians to deliver personalized care, improve patient outcomes, and advance our understanding of complex hormonal conditions.
AI-driven chatbots like Artificial Intelligence Diabetes Assistant (AIDA), ChatGPT, Emile, X2AI, and JEDi implement natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to analyse patients’ queries and provide logical answers to resolve them.
Telehealth Services
In telehealth services, patients and healthcare professionals exchange health information through electronic communication. Telephone calls, video conversations through Google Meet or Zoom and instant messages via apps are some of the most common communication mediums in telehealth.
This digital interface is a great help for patients as it is cost-effective, removes logistic barriers and enables them to receive expert guidance even in the remotest corner of the country.
DTx Programs
Digital Therapeutics (DTx) Programs for diabetes management implement software-driven evidence-based therapeutic interventions to control and attempt diabetes remission. These Programs utilise mobile devices, diabetes apps, sensors, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things to help patients in self-management of symptoms and improve their quality of life.
According to an internal survey by Fitterfly (Reimagining Diabetes Care Report 2022) involving 3000 participants, 12% of the members selected DTx programs as the first line of treatment for managing diabetes. Moreover, Fitterfly’s Real-world Effectiveness Evaluation for the diabetes CGM DTx program involving 109 participants came up with the following facts:
- A 1.2% reduction in HbA1C levels among 85% of members.
- An average reduction of 2.6% in HbA1C levels for those with initial HbA1c levels >9%.
- A 7.1% improvement in Time in Range (TIR) from a baseline value of 57.5% to 64.6%.
- An 8.7% reduction in Time above Range (TAR) from a baseline value of 36.7% to 28.1%.
- A significant correlation between high engagement with the Fitterfly wellness app and weight reduction in participants.
Role of Regulators in Managing Diabetes Digital App Technology
Regulators play a crucial role in governing and improving the awareness related to digital technology uses in diabetes management.
European Medicines Agency (EMA)
EMA recognises mobile apps as medical devices if they help in diagnosis or therapeutic purposes. In 2014, it released the ‘Communication on Digital Transformation of Health and Care’ for empowering patients and establishing a healthier society. It listed three priorities in this publication:
- Enable citizens to access their health information throughout the EU.
- Validate researchers to pool data, expertise, computing processing and storage capacities across the EU.
- Empower individuals via digital tools for user feedback and person-centred care.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The Digital Health Center of Excellence under the FDA endorses empowering patients by introducing responsible and high-quality digital health innovation. It listed the following objectives to foster digital health:
- Connect and develop partnerships to expedite digital health advancements.
- Share knowledge to enhance awareness, motivate synergy, and implement best practices.
- Incorporate regulatory approaches for efficient and least burdensome oversight keeping in mind the FDA standards for safe and effective products.
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
ICMR published an Ethical Guidelines for Application of Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Research and Healthcare in 2023. In this publication, the regulatory body pointed out the following risk minimization and safety points for AI in healthcare:
- Significant control measures are necessary to prevent unintended or deliberate misuse of AI in healthcare.
- AI technologies should have a pre-emptive approach to risks to minimise unintended consequences and results.
- Since AI is prone to cyber-attacks, scientists should completely anonymize and delink data for final use.
- The Ethical Committee (EC) should confirm that there are favourable benefit-risk assessments. The benefits should outweigh the risks involved.
- EC should list out measures to protect and safeguard patients from stigmatization or discrimination due to the publication of their health status.
Key Takeaways
- The rapid strides of digital technology in diabetes care mark a transformative era in healthcare, promising to address longstanding challenges and enhance patient outcomes.
- Understanding and meeting patient expectations are pivotal elements in the successful navigation of healthcare professionals through the complexities of this digital era.
- The integration of digital tools in diabetes care like cloud-connected CGMs, DTx Programs and Telehealth has brought about significant improvements.
- Regulators like EMA, USFDA and ICMR play key roles in ensuring the responsible and safe integration of digital health innovations.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Want to know how can Fitterfly enhance your practice and improve patient outcomes?