Technology Revolution Redefining the Diabetes Care Experience

Abstract:
Tech-driven revolution through continuous glucose monitoring, closed-loop insulin delivery, AI-powered chatbots and virtual clinics are redefining the future of diabetes management. Though physicians and patients exhibit mixed perspectives on diabetes technology, it can reduce the global diabetes burden considerably.
Research studies will overcome its present challenges like data security, privacy concerns, cyber threats, and standardisation in technologies and protocols.
Diabetes Technology Leading a Paradigm Shift in Treatment Process
Diabetes technology is spearheading a transformative paradigm shift in treatment processes over the past few decades.
Innovative technologies in diabetes care offer continuous glucose monitoring, and improved patient self-care through empowerment, glycemic control optimisation, behaviour modifications and precise insulin delivery.
The escalating global burden of diabetes is driving scientists to develop state-of-the-art technologies to revolutionise diabetes care and enhance patients’ lives.
Physicians’ and Patients’ Perspectives on Diabetes Technology
Clinicians and patients have mixed views regarding the use of diabetes technology, as per an analysis encompassing 13 articles and 242 patients, (age 18-81 years).
Though the integration of technologies does not have any direct impact on diabetes distress scores, studies have revealed that there is a notable reduction in diabetes burden and improvement in quality of life when patients rely on technologies.
People living with diabetes become increasingly adherent to technology if they are seamless to access, implement and provide reliable information.
Physicians’ primary concerns related to implementing diabetes technology include costs, achieving adherence and attaining learning curves.
A study involving 209 clinicians highlights a generational divide, where younger health professionals harboured more positive attitudes regarding the use of diabetes technologies than senior doctors.
However, higher expenditures and lack of healthcare system coverage are major barriers for doctors and patients in implementing diabetes technology.
Latest Innovations in Diabetes Technology
Technological solutions in diabetes management provide safety, support, and self-efficacy for achieving a good glycaemic legacy and preventing complications. They target to reduce the diabetes burden by providing real-time information facilitating decisions.
The following are some of the latest diabetes technologies in use today.
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices help in determining the blood sugar of individuals at regular intervals painlessly. CGM devices are of two types- intermittently viewed CGM (iCGM) and real-time CGM (rtCGM) gadgets.
The former offers glycaemic information on demand retrospectively, while the latter provides real-time data. rtCGM integrated insulin pump also enables timely insulin infusion based on real-time glycaemic values.
Fitterfly’s 90 days Real-world Effectiveness Evaluation of its Diabetes CGM DTx Program published on JMIR Diabetes (2023;8:e43292) achieved the following results:
- A 1.2% decrease in HbA1C levels among 85% of the participants.
- An average reduction of 2.6% in HbA1C levels for those with initial HbA1c levels >9%.
- A significant correlation between high engagement with the Fitterfly wellness app and weight reduction in participants.
- Time in Range (TIR) improved by 7.1% from a baseline value of 57.5% to 64.6%.
- Time above Range (TAR) was reduced by 8.7% from a baseline value of 36.7% to 28.1%.
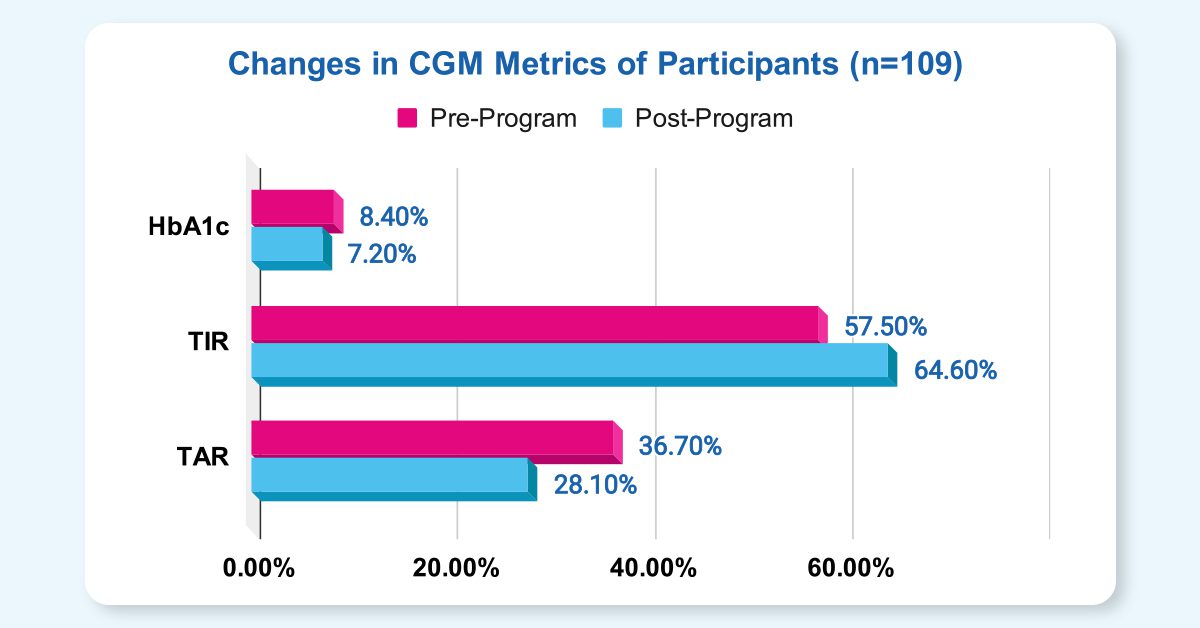
Fig: Changes in CGM Metrics among participants of the Fitterfly Diabetes CGM DTx Program.
Now scientists have also developed long-term implantable subcutaneous fluorescence-based CGM sensors which can remain active for up to 180 days. Researchers are further working to extend this duration.
2. Continuous Ketone Monitoring (CKM) by Ketone Sensors
Diabetes patients tend to develop higher levels of ketones in blood circulation, thereby increasing the release of counter-regulatory hormones, like glucagon. The hormone imbalances may lower the blood pH and can cause severe organ damage or even death.
Continuous ketone sensors significantly improve patients’ outcomes by continuously calculating the ketone in blood circulation. They determine beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) in interstitial fluid (ISF) based on wired enzyme electrochemistry technology.
Jennifer Y. Zhang et al conducted a 14-day ketone sensor study on 12 human volunteers. The gadget’s operational stability was significantly accurate with a linear response over the 0-8 mM range.
Research is going on for a possible integration of CKM and CGM devices on the same sensor platform.
3. Insulin Pumps and Closed Loop Delivery Systems
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) with the help of insulin pumps is a well-established therapeutic option, especially for managing T1DM. Though the first CSII pump came into service in 1979, present-day pumps come with a bolus calculator and automatic basal rate suspension to reduce hypoglycaemia.
A meta-analysis undertaken in 2003, involving 52 studies and 1547 participants indicated that there was a 0.8-1% drop in HbA1c level and mean blood glucose levels (in 11 studies) among members with CSII.
Currently, scientists are working towards subcutaneous closed-loop system development. These devices will fully automate all insulin delivery without any mealtime bolus inputs from users.
However, the primary challenge of a closed-loop system is postprandial hyperglycemia management, as there is no manually provided information related to the meal’s carbohydrate content and timings. Presently, STG-55 (Nikkiso, Tokyo, Japan) and its predecessor, the STG-22 are the only commercially available fully closed-loop insulin pumps.
4. Chatbots
Artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning (ML)-driven healthcare chatbots interact with patients, analyse their queries and provide logical answers. Patients consider chatbots superior to other Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSME) devices as they come with human-like characteristics.
Patients achieve higher levels of engagement and are more likely to become adherent to their treatment plans upon receiving consistent reminders and personalised guidance from AI chatbots. Artificial Intelligence Diabetes Assistant (AIDA), Chatgpt, Emile, X2AI, and JEDi are some popular diabetes care chatbots.
5. Smartphone Apps, Telemedicine and Virtual Clinics
Diabetes self-management often becomes challenging due to a lack of training, limited access to medical professionals, and hurdles in behavioural modifications. Smartphone diabetes apps available on Google Play and Apple App Store are found to deliver encouraging results in initiating sustaining behaviour changes and improving patients’ compliance.
Similarly, telemedicine and virtual diabetes clinics have shown promising results in removing geographical barriers, reducing treatment costs, and improving patient access to health care and clinical outcomes.
Challenges in Integrating Technology in Diabetes Care
Though there is great enthusiasm among both healthcare professionals and patients in implementing diabetes technology, here are a few challenges associated to it:
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The collection and storage of patients’ vital information is a critical issue. Health tech companies are working towards minimising cyber threats and data breaches.
Regulatory bodies like the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) have enforced strict guidelines so that patient safety and clinical validity never get compromised.
2. Standardization of Technologies and Protocols
The diversity of devices, data formats, and communication protocols often leads to a lack of standardisation in technologies and protocols. These hurdles make it challenging to establish a universal standard for diabetes management technology.
Standardization would facilitate the seamless exchange of information between different systems and promote interoperability.
3. Cost and Accessibility
The financial aspect of integrating technology into diabetes care is a significant hurdle. Most state-of-the-art technologies and devices come with a high implementation cost, thus making them inaccessible to a large magnitude of diabetic patients.
Scientists are working towards developing new technologies which can bring down this cost.
Summarising the Impact of Diabetes Technology on Patient Outcomes
Finally, we can say that the integration of technology in diabetes care marks a transformative shift. The latest innovations, ranging from CGM devices to advanced chatbots and closed-loop insulin delivery systems, hold the promise of empowering patients, optimising glycemic control, and preventing complications.
Since the global burden of diabetes is increasing exponentially, technological integration remains a beacon of hope. By overcoming its challenges and embracing the potential of innovative solutions, the future of diabetes care holds the promise of improved patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
The blog highlights the impact of the latest diabetes technology in streamlining treatment. Here are the key takeaways:
- The integration of technology in diabetes care empowers patients, optimises glycemic control, and holds the potential to prevent complications.
- The perspectives of physicians and patients reflect a dynamic landscape. Patients’ adherence is influenced by factors such as seamless access, ease of implementation, and the provision of reliable information.
- CGM devices, ketone sensors, insulin pumps, chatbots, smartphone apps and telemedicine are some of the latest innovations in diabetes technology.
- Data security, privacy concerns, cyber threats, standardisation in technologies and protocols, and cost factors are some of the primary challenges in diabetes technology.
This blog provides general information for educational and informational purposes only and shouldn't be seen as professional advice.
Want to know how can Fitterfly enhance your practice and improve patient outcomes?





















