Everything You Need to Know About Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that is characterized by high blood sugar levels. When undiagnosed and untreated, diabetes can cause several complications in the body and affect the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and heart.
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent metabolic conditions in the world today. According to an ICMR study published in the Lancet, India has over 101 million people living with diabetes in 2023, compared to 70 million in 2019. Around 136 million people, or 15.3% of the population, have prediabetes.
These statistics clearly show why India is the diabetes capital of the world today! Awareness about diabetes, its types, and how the disease develops and is managed is a powerful tool that can help reduce the incidence of this condition and the number of people affected by it.
Let’s learn more about diabetes in this informative blog!
Types of Diabetes?
When you hear diabetes, you most likely refer to type 2 diabetes or diabetes mellitus. However, there are many more types of the condition. Let’s take a look:
1. Type 1 (Juvenile diabetes)
In people with type 1 diabetes, the body produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps blood sugar enter the cells in the body for energy. When there is deficient insulin, the blood sugar levels rise, causing damage to several organs and complications.
Since this condition usually develops in children, teens and young adults, type 1 diabetes is also called juvenile diabetes. Around 5% to 10% of people with diabetes have this type of condition. It is far less common than diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes).
2. Type 2 (diabetes mellitus)
This is a chronic lifestyle condition in which the body either does not produce sufficient insulin, or the body cells are resistant to the hormone. As a result, blood sugar levels are high in individuals with this condition.
Diabetes Reversal
Calculator
To know your chances of Diabetes reversal, take the Diabetes Reversal Test
3. Gestational diabetes
This form of diabetes is diagnosed in pregnant women and is characterised by high blood sugar levels. Most women do not have any symptoms and are diagnosed during routine blood tests performed during the various trimesters of pregnancy. Women who develop gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in adults (LADA)
Also called type 1.5 diabetes due to its similarity to type 1 diabetes. Unlike type 1 diabetes, people with LADA see a worsening of symptoms slowly over a period of time. They may also need treatment for several months or years after diagnosis. Symptoms of LADA usually show up a little later in life, around 30 years.
5. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
This type of diabetes is rare and shows up when an individual is a young adult or an adolescent. MODY occurs due to a genetic mutation that affects how well the body makes insulin. When there isn’t sufficient insulin, your blood sugar levels rise.
6. Neonatal diabetes
Neonatal diabetes mellitus occurs due to a single gene mutation that occurs in children who are less than 6 months of age. This diabetes is also called congenital diabetes or diabetes of infancy.
Early treatment with medications like sulfonyl urea may improve neurological outcomes. Other causes of this type of diabetes include infections, stress, and inadequate pancreatic insulin production in preterm infants.
There are some other forms of diabetes, such as:
- Drug-induced
- Secondary
- Diabetes due to genetic disorders, and
- Pancreatic Diabetes
Any form of uncontrolled diabetes can become brittle diabetes, which is characterised by wide variations in blood sugar levels. People with this form of diabetes quickly go from hyperglycemia to hypoglycemia, and these episodes are hard to predict. Brittle diabetes is also called labile diabetes.
What are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
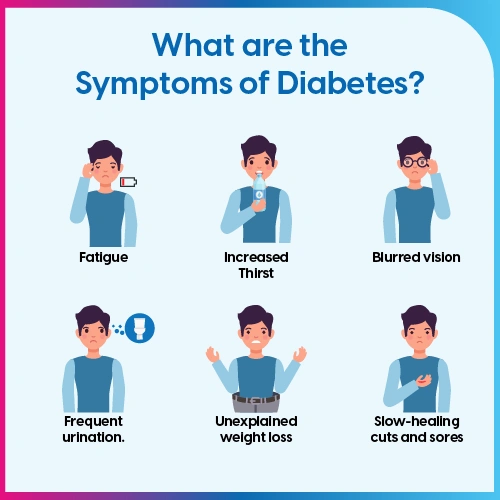

In most cases, diabetes does not cause symptoms, especially in the early stages. While the symptoms of diabetes are largely similar, there may be slight variations. Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Feeling thirsty often
- Feeling excessively hungry
- Increased fatigue and tiredness
- Blurry vision
- Delayed wound healing
- Increased weight loss
- Tingling or numbness in the extremities
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually appear suddenly among children, teens or young adults, whereas the symptoms of type 2 diabetes appear slowly over a long period of time in older individuals.
1. Symptoms of Prediabetes
Besides the typical signs of diabetes, acanthosis nigricans is a sign of insulin resistance. It is the development of dark, thick, velvety patches of skin in areas like elbows, knees, neck, and armpits.
2. Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Women with gestational diabetes usually do not show any signs or symptoms. For this reason, it is important for them to measure their blood sugar levels regularly during their pregnancy. Persistent UTIs, macrosomia, and polyhydramnios may be some signs of gestational diabetes that prompt obstetricians to perform additional tests.
3. Symptoms of LADA
Individuals with LADA may show the same signs as those with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Some, however, may be asymptomatic.
It is natural to wonder if symptoms of diabetes in men and women. While most signs and symptoms are the same in both genders, slight differences may exist. A few signs and symptoms in men include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Genital thrush ( a type of fungal infection)
- Reduced muscle mass
A few symptoms that may be seen in women living with diabetes include:
- Vaginal fungal infections (like Candida)
- Quent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Menstrual irregularities
- Sexual dysfunction
- Fertility issues
What Causes Diabetes?
The causes of diabetes vary for each subtype:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
While the exact cause of this form of diabetes is unknown, it is believed to arise due to an autoimmune reaction wherein the body cells destroy the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. Some people inherit genes that increase their likelihood of developing this condition.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
A few common causes of type 2 diabetes include being overweight or obese, insulin resistance, family history and genetic changes.
3. Gestational diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body undergoes hormonal changes like weight gain. Due to these physiological changes, the body’s cells become immune to insulin, leading to gestational diabetes.
4. LADA
LADA occurs when the body makes antibodies against the body’s immune system and attacks the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. Due to this, the body loses its ability to form insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
5. Prediabetes
The causes of prediabetes are similar to diabetes. The two primary causes of prediabetes include insulin resistance and metabolic disturbance.
What are the Risk factors of Diabetes?
Like the causes, the risk factors for various types of diabetes vary:
1. Type 1
The risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as those for type 2. A few known risk factors include:
- Family history: Having a first-degree relative like a parent, brother or sister with type 1 diabetes increases your risk of developing the condition.
- Age: While you can get type 1 diabetes at any age, it usually develops in children, teens and young adults.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Since type 2 diabetes develops during one’s lifetime, the risk factors are clearer and include the following:
- Having prediabetes
- Being overweight or obese
- Being 45 years or older
- Having a parent, brother or sister with the condition
- Physically inactive
- History of gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby who weighs over 4 kg
- Personal history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
3. Gestational diabetes
You may be at risk of developing gestational diabetes if:
- You have a history of gestational diabetes in your previous pregnancy
- Are overweight or obese
- Over 25 years of age
- Have PCOS or related hormonal disorder
4. Prediabetes
You may be at risk of developing prediabetes if you have the following:
- If you are overweight or obese
- Are 45 years or older
- Have a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes
- Are physically active less than three days a week
- Have had gestational diabetes
5. LADA
Some factors or a combination of them that increase the risk of developing LADA include:
- Obesity or excessive weight
- Low birth weight
- Low physical activity
- Psychosocial stress
Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled and untreated diabetes can result in several complications. These are called diabetes-related complications. Diabetes-related complications can be of two types- acute and chronic.
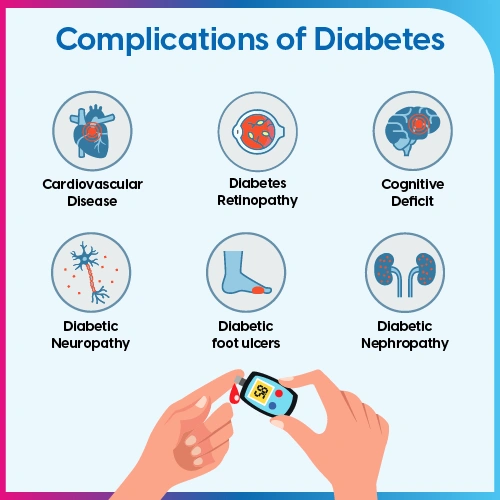

Chronic complications of diabetes develop over a long period of time and include:
- Eye-related problems (diabetic retinopathy)
- Foot problems that stem from nerve damage and may result in amputation if untreated
- Cardiovascular problems like heart disease and stroke
- Kidney problems (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
- Gum disease
- Sexually and fertility problems in men and women
Acute complications of diabetes develop anytime and can lead to chronic complications. These include:
- Hypoglycemia: Lower than normal blood sugar levels
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS): A life-threatening emergency that happens in people with type 2 diabetes. It usually develops when an individual is dehydrated with very high blood sugar levels.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: A life-threatening emergency which results in a dangerously-high build-up of ketones in the blood.
How Can Diabetes be Diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects you to have diabetes, they may recommend a few tests to confirm their diagnosis. The three most common tests to diagnose diabetes include:
1. Fasting blood glucose level test
This blood test is performed after 8 to 12 hours of an overnight fast. If your test results are 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate occasions, you are said to have diabetes.
2. HbA1C test
This test gives the average of your blood sugar levels over three months. You are diagnosed with diabetes if your HbA1c levels are 6.5% or higher.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
This blood test is performed two hours after consuming a special sugar drink containing 75 gm of glucose. If your blood sugar levels are 200 mg/dL or higher after 2 hours of drinking the liquid; you are diagnosed with diabetes.
Diabetes screening is recommended for the following individuals:
- Individuals (adults and children) who are overweight
- Individuals with other risk factors like high blood pressure, PCOS, infertility
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with the tests mentioned above during each trimester.
Diabetes in Children
When we discuss diabetes, most often, we do so with reference to adults. However, children are not immune to this chronic condition. While type 1 diabetes was the more common diabetes in children until recently, type 2 diabetes (also called adult-onset diabetes) is becoming increasingly common in this age group. This has to do primarily with the rise in obesity and unhealthy lifestyles prevalent among children today.
The risk factors and the presentation of diabetes in children are similar to those found in adults. To help lower the risk and incidence of diabetes in children, here are a few tips that parents should keep in mind:
- Help them maintain a healthy weight
- Ensure they are physically active and get ample outdoor playtime
- Have them eat smaller portions of healthy food
- Limit their screen times
The management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children may vary. While type 2 diabetes can be controlled with diet and exercise, most children with type 1 diabetes need not take insulin. They, however, still require regular monitoring of their blood sugar levels.
How Can Diabetes Be Treated and Managed?
The treatment and management of diabetes, regardless of the type, has one goal– bringing your blood sugar levels within the normal range and preventing diabetes-related complications.
1. Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, you may need insulin shots daily or to wear an insulin pump. This ensures you get your regular dosage of the hormone to keep your blood sugar levels within the normal range. The type, form and dosage of insulin will be determined for your condition by your diabetologist. You will also require lifestyle modifications along with insulin.
2. Type 2 diabetes
The management of type 2 diabetes includes medications and lifestyle modifications, such as:
-
- Losing excess weight and managing to keep it within the optimal range
- Healthy eating, preferably a diet plan curated for you by your nutritionist
- Getting a minimum of 30 minutes of aerobic exercise
- Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels
3. LADA
Most individuals with LADA are often diagnosed to have type 2 diabetes, and therefore, a majority of them initially get treated using metformin. If LADA has been identified, further tests are conducted to determine the level of c-peptide (a biological marker for LADA). The level of this marker helps your doctor determine the right kind of medicine to help manage LADA.
4. Prediabetes
If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes, you can work with your doctor and diabetes care team to reverse the condition permanently. Management of prediabetes usually involves the following:
- Eat a healthy diet
- Be more active
- Lose excess weight and maintain it within the optimal range
- Take medications (if any) as prescribed by your doctor
- Quit smoking and alcohol consumption
- Focus on getting a minimum of 7 to 9 hours of sleep
- If you are under stress, find ways to effectively manage your stress levels, such as yoga, meditation, mindfulness or pursuing a hobby
5. Gestational diabetes
The management of gestational diabetes is similar to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Your obstetrician will work closely with a diabetologist to ensure your blood sugar levels are brought under control without affecting your or your baby’s health.
How Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
Diabetes is a preventable condition in most cases. Even individuals with insulin resistance or prediabetes can prevent the progress of their condition to a full-blown diabetes condition.
Here are simple ways to prevent diabetes:
1. Effective weight management
Excess weight and obesity are high-risk factors for diabetes. Reducing weight and maintaining it within the normal range goes a long way in preventing diabetes.
2. Get moving
Being physically inactive is a contributing factor to diabetes. Getting 150 minutes of exercise a week or 30 minutes a day is important to control your blood sugar levels.
3. Focus on your diet
People with insulin resistance and prediabetes must work with a nutritionist to ensure they are eating a healthy, balanced diet that helps control their blood sugar levels. A few dietary tips to prevent diabetes include– choosing whole grains, increasing your protein content in every meal, skipping sugary beverages and foods, picking healthy fats and limiting your consumption of red and processed meat.
4. Quit smoking and alcohol
Smoking and alcohol consumption can increase your risk of developing diabetes. Staying clear of them can reduce your likelihood of developing the condition.
What is the Prognosis for Diabetes?
Diabetes, except gestational diabetes, is a chronic condition that can be managed but not cured. While some people with diabetes may require medications to help them control their blood sugar levels, others may no longer need medication support if they can reduce their weight, maintain it within the normal range, and stay physically active.
Diabetes has a good prognosis in individuals who work with their diabetes care team to send their condition into remission and maintain it for a prolonged period of time.
When Should you see a Doctor for Diabetes?
Ideally, the best time to visit a doctor for diabetes is when you are diagnosed with the condition. Infact, you must visit a doctor if you have been diagnosed with prediabetes, as the condition can be reversed.
Once diagnosed, you must work closely with your doctor and your diabetes care team to ensure your blood sugar levels are within the normal range at all times.
Regular diabetes monitoring at home and by your doctor, along with a team of experts like a nutritionist, fitness expert and success coach, can help send your diabetes into remission and significantly improve your quality of life.
FitterTake
While type 2 diabetes is a widely prevalent disease today, diabetes can be of several different types, affecting various age groups. While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that develops over your lifetime, type 1 is caused due to autoimmunity.
Regardless of the type of diabetes, each one needs management to prevent complications. Working with a team of experts is important to maintain your blood sugar levels within the normal range.
At Fitterfly, we understand diabetes like no other. Fitterfly’s Diabetes Care Program is driven by technology, backed by science and curated by expert diabetologists, nutritionists, fitness experts and success coaches to empower you to manage your blood sugar levels and live a good quality of life.
You can also sign up for our program to know more/ Wish to know more? Sign up for our program. To speak with us, just give us a missed call at 08069450746, and we will definitely get back to you.
Don’t struggle alone & get the expert care you deserve